Page 206 -
P. 206
11 - PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT
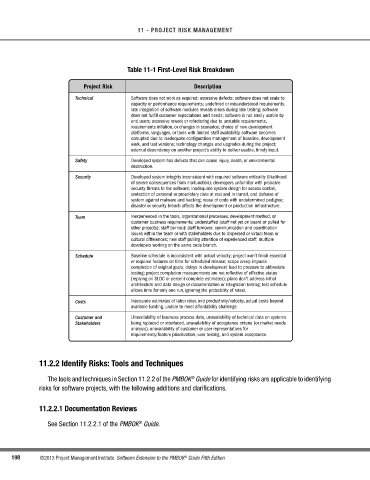
Table 11-1 First-Level Risk Breakdown
Project Risk Description
Technical Software does not work as required: excessive defects; software does not scale to
capacity or performance requirements; undefined or misunderstood requirements;
late integration of software modules reveals errors during late testing; software
does not fulfill customer expectations and needs; software is not easily usable by
end users; excessive rework or refactoring due to unstable requirements,
requirements inflation, or changes in scenarios; choice of new development
platforms, languages, or tools with limited staff availability, software becomes
corrupted due to inadequate configuration management of baseline, development
work, and test versions; technology changes and upgrades during the project;
external dependency on another project's ability to deliver usable, timely input.
Safety Developed system has defects that can cause injury, death, or environmental
destruction.
Security Developed system integrity inconsistent with required software criticality (likelihood
of severe consequences from malfunction); developers unfamiliar with probable
security threats to the software; inadequate system design for access control,
protection of personal or proprietary data at rest and in transit, and defense of
system against malware and hacking; reuse of code with undetermined pedigree;
disaster or security breach affects the development or production infrastructure.
Team Inexperienced in the tools, organizational processes, development method, or
customer business requirements; understaffed (staff not yet on board or pulled for
other projects); staff burnout; staff turnover; communication and coordination
issues within the team or with stakeholders due to dispersed or virtual team or
cultural differences; new staff pulling attention of experienced staff; multiple
developers working on the same code branch.
Schedule Baseline schedule is inconsistent with actual velocity; project won't finish essential
or required features on time for scheduled release; scope creep impacts
completion of original goals; delays in development lead to pressure to abbreviate
testing; project completion measurements are not reflective of effective status
(replying on SLOC or percent complete estimates); plans don't address initial
architecture and data design or documentation or integration testing; test schedule
allows time for only one run, ignoring the probability of retest.
Costs Inaccurate estimates of labor rates and productivity/velocity, actual costs beyond
available funding, unable to meet affordability challenge.
Customer and Unavailability of business process data, unavailability of technical data on systems
Stakeholders being replaced or interfaced, unavailability of acceptance criteria (or market needs
analysis), unavailability of customer or user representatives for
requirements/feature prioritization, user testing, and system acceptance.
11.2.2 Identify Risks: Tools and Techniques
®
The tools and techniques in Section 11.2.2 of the PMBOK Guide for identifying risks are applicable to identifying
risks for software projects, with the following additions and clarifications.
11.2.2.1 Documentation Reviews
®
See Section 11.2.2.1 of the PMBOK Guide.
198 ©2013 Project Management Institute. Software Extension to the PMBOK Guide Fifth Edition
®