Page 136 - Software and Systems Requirements Engineering in Practice
P. 136
104 S o f t w a r e & S y s t e m s R e q u i r e m e n t s E n g i n e e r i n g : I n P r a c t i c e
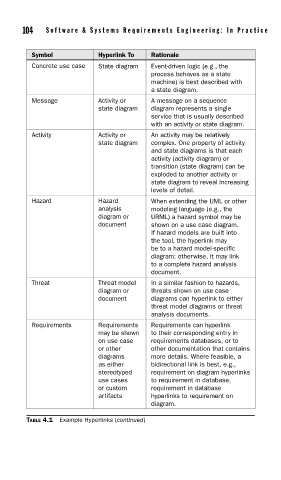
Symbol Hyperlink To Rationale
Concrete use case State diagram Event-driven logic (e.g., the
process behaves as a state
machine) is best described with
a state diagram.
Message Activity or A message on a sequence
state diagram diagram represents a single
service that is usually described
with an activity or state diagram.
Activity Activity or An activity may be relatively
state diagram complex. One property of activity
and state diagrams is that each
activity (activity diagram) or
transition (state diagram) can be
exploded to another activity or
state diagram to reveal increasing
levels of detail.
Hazard Hazard When extending the UML or other
analysis modeling language (e.g., the
diagram or URML) a hazard symbol may be
document shown on a use case diagram.
If hazard models are built into
the tool, the hyperlink may
be to a hazard model-specific
diagram; otherwise, it may link
to a complete hazard analysis
document.
Threat Threat model In a similar fashion to hazards,
diagram or threats shown on use case
document diagrams can hyperlink to either
threat model diagrams or threat
analysis documents.
Requirements Requirements Requirements can hyperlink
may be shown to their corresponding entry in
on use case requirements databases, or to
or other other documentation that contains
diagrams more details. Where feasible, a
as either bidirectional link is best, e.g.,
stereotyped requirement on diagram hyperlinks
use cases to requirement in database,
or custom requirement in database
artifacts hyperlinks to requirement on
diagram.
TABLE 4.1 Example Hyperlinks (continued)