Page 113 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 113
100 Soil and Water Contamination
1.40
6642 6642 6642
Water oxidised
1.20 2+
FeOH
+
Fe(OH)
1.00 3+ 2
Fe
0.80
0.60
2+ Fe(OH)
Fe 3
0.40
Eh (Volt) 0.20
0.00 Fe(OH) -
4
-0.20
FeS 2
2+
Fe
-0.40 FeO
-0.60
FeS
0
Fe
-0.80
Water reduced
-1.00
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
pH
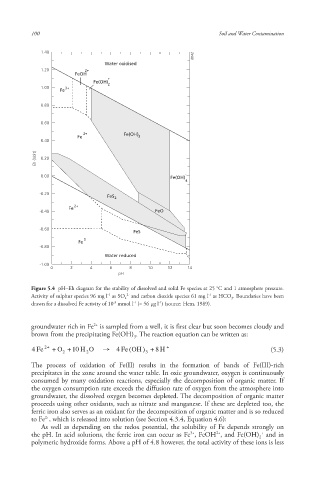
Figure 5.4 pH–Eh diagram for the stability of dissolved and solid Fe species at 25 °C and 1 atmosphere pressure.
-1
-1
2-
Activity of sulphur species 96 mg l as SO 4 and carbon dioxide species 61 mg l as HCO 3 . Boundaries have been
-1
-3
-1
drawn for a dissolved Fe activity of 10 mmol l (= 56 μg l ) (source: Hem, 1989).
2+
groundwater rich in Fe is sampled from a well, it is first clear but soon becomes cloudy and
brown from the precipitating Fe(OH) . The reaction equation can be written as:
3
4 Fe 2 + + O 2 +10 H 2 O 4 Fe ( OH ) 3 + H + (5.3)
8
The process of oxidation of Fe(II) results in the formation of bands of Fe(III)-rich
precipitates in the zone around the water table . In oxic groundwater, oxygen is continuously
consumed by many oxidation reactions, especially the decomposition of organic matter . If
the oxygen consumption rate exceeds the diffusion rate of oxygen from the atmosphere into
groundwater, the dissolved oxygen becomes depleted. The decomposition of organic matter
proceeds using other oxidants , such as nitrate and manganese . If these are depleted too, the
ferric iron also serves as an oxidant for the decomposition of organic matter and is so reduced
2+
to Fe , which is released into solution (see Section 4.3.4, Equation 4.6):
As well as depending on the redox potential , the solubility of Fe depends strongly on
+
2+
3+
the pH . In acid solutions, the ferric iron can occur as Fe , FeOH , and Fe(OH) and in
2
polymeric hydroxide forms. Above a pH of 4.8 however, the total activity of these ions is less
10/1/2013 6:44:25 PM
Soil and Water.indd 112
Soil and Water.indd 112 10/1/2013 6:44:25 PM