Page 353 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 353
340 Soil and Water Contamination
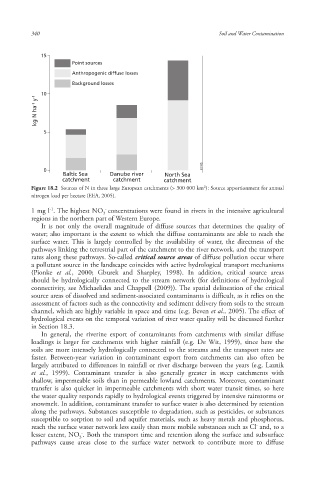
Figure 18.2 Sources of N in three large European catchments (> 300 000 km²): Source apportionment for annual
nitrogen load per hectare (EEA, 2005).
-1
-
1 mg l . The highest NO concentrations were found in rivers in the intensive agricultural
3
regions in the northern part of Western Europe.
It is not only the overall magnitude of diffuse sources that determines the quality of
water; also important is the extent to which the diffuse contaminants are able to reach the
surface water. This is largely controlled by the availability of water, the directness of the
pathways linking the terrestrial part of the catchment to the river network, and the transport
rates along these pathways. So-called critical source areas of diffuse pollution occur where
a pollutant source in the landscape coincides with active hydrological transport mechanisms
(Pionke et al., 2000; Gburek and Sharpley, 1998). In addition, critical source areas
should be hydrologically connected to the stream network (for definitions of hydrological
connectivity, see Michaelides and Chappell (2009)). The spatial delineation of the critical
source areas of dissolved and sediment-associated contaminants is difficult, as it relies on the
assessment of factors such as the connectivity and sediment delivery from soils to the stream
channel, which are highly variable in space and time (e.g. Beven et al., 2005). The effect of
hydrological events on the temporal variation of river water quality will be discussed further
in Section 18.3.
In general, the riverine export of contaminants from catchments with similar diffuse
loadings is larger for catchments with higher rainfall (e.g. De Wit, 1999), since here the
soils are more intensely hydrologically connected to the streams and the transport rates are
faster. Between-year variation in contaminant export from catchments can also often be
largely attributed to differences in rainfall or river discharge between the years (e.g. Laznik
et al., 1999). Contaminant transfer is also generally greater in steep catchments with
shallow, impermeable soils than in permeable lowland catchments. Moreover, contaminant
transfer is also quicker in impermeable catchments with short water transit times, so here
the water quality responds rapidly to hydrological events triggered by intensive rainstorms or
snowmelt. In addition, contaminant transfer to surface water is also determined by retention
along the pathways. Substances susceptible to degradation, such as pesticides, or substances
susceptible to sorption to soil and aquifer materials, such as heavy metals and phosphorus,
-
reach the surface water network less easily than more mobile substances such as Cl and, to a
-
lesser extent, NO . Both the transport time and retention along the surface and subsurface
3
pathways cause areas close to the surface water network to contribute more to diffuse
10/1/2013 6:47:10 PM
Soil and Water.indd 352
Soil and Water.indd 352 10/1/2013 6:47:10 PM