Page 28 - Standard Handbook Petroleum Natural Gas Engineering VOLUME2
P. 28
16 Resen
8
.E
Pseudo reduced pressure
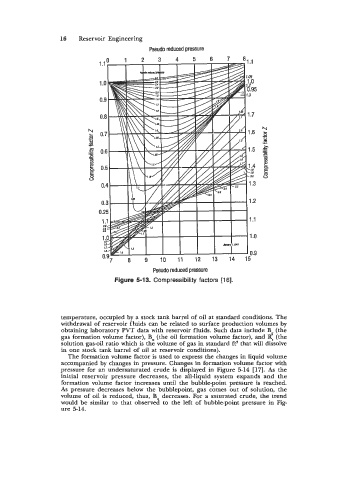
Figure 5-13. Compressibility factors [16].
temperature, occupied by a stock tank barrel of oil at standard conditions. The
withdrawal of reservoir fluids can be related to surface production volumes by
obtaining laboratory PVT data with reservoir fluids. Such data include Bg (the
gas formation volume factor), Bo (the oil formation volume factor), and R, (the
solution gas-oil ratio which is the volume of gas in standard ft3 that will dissolve
in one stock tank barrel of oil at reservoir conditions).
The formation volume factor is used to express the changes in liquid volume
accompanied by changes in pressure. Changes in formation volume factor with
pressure for an undersaturated crude is displayed in Figure 5-14 [17]. As the
initial reservoir pressure decreases, the all-liquid system expands and the
formation volume factor increases until the bubble-point pressure is reached.
As pressure decreases below the bubblepoint, gas comes out of solution, the
volume of oil is reduced, thus, Bo decreases. For a saturated crude, the trend
would be similar to that observed to the left of bubble-point pressure in Fig-
ure 5-14.