Page 29 - Standard Handbook Petroleum Natural Gas Engineering VOLUME2
P. 29
Basic Principles, Definitions, and Data 17
1.40
m
5
1.30
d
E
d
y 1.20
3
P
z
z 1.10
2
E
1 .oo
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500
PRESSURE, PSlA
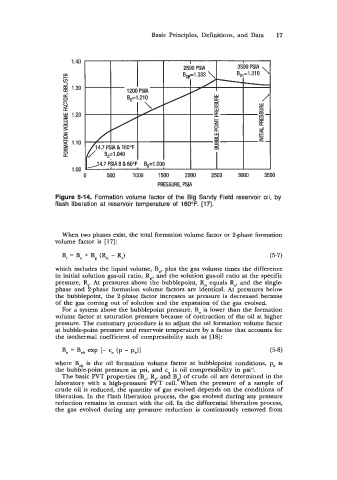
Figure 5-14. Formation volume factor of the Big Sandy Field reservoir oil, by
flash liberation at reservoir temperature' of 160°F. [17].
When two phases exist, the total formation volume factor or 2-phase formation
volume factor is [17]:
Bt = Bo + Bg (Rsi - RJ (5-7)
which includes the liquid volume, Bo, plus the gas volume times the difference
in initial solution gas-oil ratio, Rsi, and the solution gas-oil ratio at the specific
pressure, RS. At pressures above the bubblepoint, Rsi equals Rs, and the single-
phase and 2-phase formation volume factors are identical. At pressures below
the bubblepoint, the 2-phase factor increases as pressure is decreased because
of the gas coming out of solution and the expansion of the gas evolved.
For a system above the bubblepoint pressure, Bo is lower than the formation
volume factor at saturation pressure because of contraction of the oil at higher
pressure. The customary procedure is to adjust the oil formation volume factor
at bubble-point pressure and reservoir temperature by a factor that accounts for
the isothermal coefficient of compressibility such as [ 181:
Bo = Bob exp 1- '0 (p - p,)] (5-8)
where Bob is the oil formation volume factor at bubblepoint conditions, pb is
the bubble-point pressure in psi, and co is oil compressibility in psi-'.
The basic PVT properties (Bo, Rs, and BJ of crude oil are determined in the
laboratory with a high-pressure PVT cell. When the pressure of a sample of
crude oil is reduced, the quantity of gas evolved depends on the conditions of
liberation. In the flash liberation process, the gas evolved during any pressure
reduction remains in contact with the oil. In the differential liberation process,
the gas evolved during any pressure reduction is continuously removed from