Page 173 - Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology
P. 173
Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology - Chapter 6
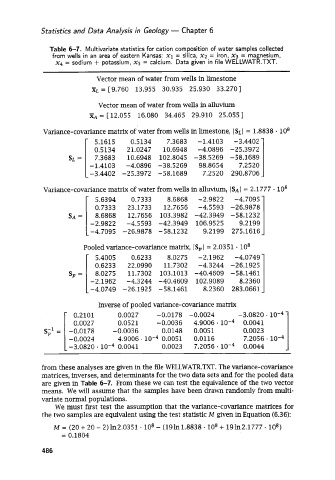
Table 6-7. Multivariate statistics for cation composition of water samples collected
from wells in an area of eastern Kansas: x1 = silica, x2 = iron, XJ = magnesium,
x4 = sodium + potassium, xg = calcium. Data given in file WELLWATR.TXT.
Vector mean of water from wells in limestone
XL = [ 9.760 13.955 30.935 25.930 33.2701
Vector mean of water from wells in alluvium
XA = [ 12.055 16.080 34.465 29.910 25.055 ]
SL= I 21.0247 10.6948 -1.4103 -3.4402
Variance-covariance matrix of water from wells in limestone, ISL I = 1.8838 - lo8
7.3683
0.5134
5.1615
-4.0896 -25.3972
0.5134
10.6948 102.8045 -38.5269
7.3683
-1.4103 -4.0896 -38.5269 98.8654 -58.1689 1
7.2520
-3.4402 -25.3972 -58.1689 7.2520 290.8706
Variance-covariance matrix of water from wells in alIuvium, IsAI = 2.1777 - lo8
I 23.1733 12.7656 -4.5593 -26.9878 1
5.6394
-4.7095
8.6868
0.7333
-2.9822
0.7333
12.7656 103.3982 -42.3949 -58.1232
8.6868
SA = -2.9822 -4.5593 -42.3949 106.9525 9.2199
-4.7095 -26.9878 -58.1232
9.2199 275.1616
Pooled variance-covariance matrix, ISPI = 2.0351 lo8
5.4005 0.6233 8.0275 -2.1962 -4.0749
0.6233 22.0990 11.7302 -4.3244 -26.1925
Sp = 8.0275 11.7302 103.1013 -40.4609 -58.1461
-2.1962 -4.3244 -40.4609 102.9089 8.2360
I -4.0749 -26.1925 -58.1461 8.2360 283.0661
Inverse of pooled variance-covariance matrix
0.2101 0.0027 -0.0178 -0.0024 -3.0820 -
0.0027 0.0521 -0.0036 4.9006 . 0.0041
s-1 = -0.0178 -0.0036 0.0148 0.0051 0.0023
P 7.2056 .
-0.0024 4.9006. lom4 0.0051 0.0116
-3.0820 lo-* 0.0041 0.0023 7.2056 - 0.0044
from these analyses are given in the file WELLWATR.TXT. The variance-covariance
matrices, inverses, and determinants for the two data sets and for the pooled data
are given in Table 6-7. From these we can test the equivalence of the two vector
means. We will assume that the samples have been drawn randomly from multi-
variate normal populations.
We must first test the assumption that the variance-covariance matrices for
the two samples are equivalent using the test statistic M given in Equation (6.36):
M = (20 + 20 - 2)1n2.0351. lo8 - (19ln1.8838. lo8 + 19h2.1777. lo8)
= 0.1804
486