Page 65 - Synthetic Fuels Handbook
P. 65
NATURAL GAS 53
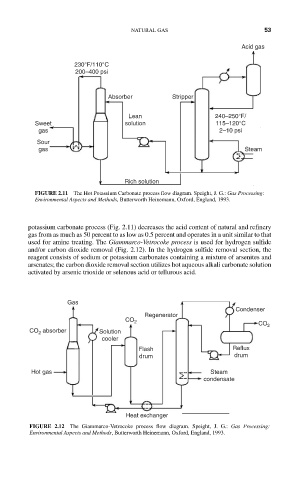
Acid gas
230°F/110°C
200–400 psi
Absorber Stripper
Lean 240–250°F/
Sweet solution 115–120°C
gas 2–10 psi
Sour
gas Steam
Rich solution
FIGURE 2.11 The Hot Potassium Carbonate process flow diagram. Speight, J. G.: Gas Processing:
Environmental Aspects and Methods, Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, England, 1993.
potassium carbonate process (Fig. 2.11) decreases the acid content of natural and refinery
gas from as much as 50 percent to as low as 0.5 percent and operates in a unit similar to that
used for amine treating. The Giammarco-Vetrocoke process is used for hydrogen sulfide
and/or carbon dioxide removal (Fig. 2.12). In the hydrogen sulfide removal section, the
reagent consists of sodium or potassium carbonates containing a mixture of arsenites and
arsenates; the carbon dioxide removal section utilizes hot aqueous alkali carbonate solution
activated by arsenic trioxide or selenous acid or tellurous acid.
Gas
Condenser
Regenerator
CO 2 CO
CO absorber Solution 2
2
cooler
Flash Reflux
drum drum
Hot gas Steam
condensate
Heat exchanger
FIGURE 2.12 The Giammarco-Vetrocoke process flow diagram. Speight, J. G.: Gas Processing:
Environmental Aspects and Methods, Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, England, 1993.