Page 64 - Synthetic Fuels Handbook
P. 64
52 CHAPTER TWO
to enhance the methanol recovery. The IFPEXOL-2 process for acid gas removal is very
similar to an amine-type process except for the operating temperatures. The absorber
operates below −20°F to minimize methanol losses, and the regenerator operates at about
90 psi. Cooling is required on the regenerator condenser to recover the methanol. This pro-
cess usually follows the IFPEXOL-1 process so excessive hydrocarbon absorption is not
as great a problem (Minkkinen and Jonchere, 1997).
2.7.5 Carbonate-Washing and Water-Washing Processes
Carbonate washing is a mild alkali process for emission control by the removal of acid
gases (such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide) from gas streams (Speight, 1993,
2007b) and uses the principle that the rate of absorption of carbon dioxide by potassium
carbonate increases with temperature. It has been demonstrated that the process works best
near the temperature of reversibility of the reactions:
K CO + CO + H O → 2KHCO
2 3 2 2 3
K CO + H S → KHS + KHCO 3
2
3
2
Water washing, in terms of the outcome, is analogous to washing with potassium
carbonate (Kohl and Riesenfeld, 1985), and it is also possible to carry out the desorption
step by pressure reduction. The absorption is purely physical and there is also a relatively
high absorption of hydrocarbons, which are liberated at the same time as the acid gases.
The process using potassium phosphate is known as phosphate desulphurization, and it
is used in the same way as the Girbotol process to remove acid gases from liquid hydrocar-
bons as well as from gas streams. The treatment solution is a water solution of tripotassium
phosphate (K PO ), which is circulated through an absorber tower and a reactivator tower
3
4
in much the same way as the ethanolamine is circulated in the Girbotol process; the solution
is regenerated thermally.
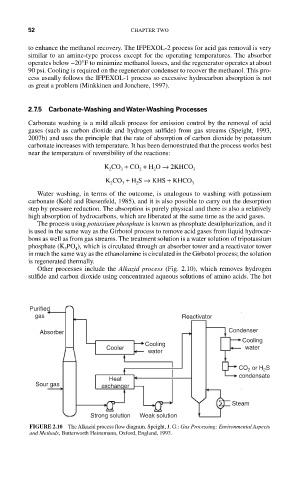
Other processes include the Alkazid process (Fig. 2.10), which removes hydrogen
sulfide and carbon dioxide using concentrated aqueous solutions of amino acids. The hot
Purified
gas Reactivator
Absorber Condenser
Cooling
Cooling
Cooler water
water
CO or H S
2
2
condensate
Heat
Sour gas exchanger
Steam
Strong solution Weak solution
FIGURE 2.10 The Alkazid process flow diagram. Speight, J. G.: Gas Processing: Environmental Aspects
and Methods, Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, England, 1993.