Page 115 -
P. 115
82 Part 1 • SyStemS analySiS FundamentalS
Expediting can make or break a successful project. The systems analyst has to remain on top
of the situation by managing the project throughout the entire development process. The analyst
needs to make sure that the project costs are managed properly.
Controlling Costs Using Earned Value Management
Once a systems analyst has an approved budget, it is imperative that the analyst keeps it updated
so the project doesn’t exceed the budget as it progresses. The baseline needs to be continually
revised, and all the stakeholders need to be informed.
Often changes occur in the middle of a project. The client may request new features, or new
technologies may be introduced that will change the way the system is developed. No matter
what these changes are, the budget needs to be revised.
One tool available to systems analysts is earned value management (EVM). It is a technique
used to help determine progress (or setbacks) on a project and involves project cost, the project
schedule, and the performance of the project team. The four key measures in earned value man-
agement are:
• Budget at completion (BAC) is the total budget for the project, from the beginning until
completion. If you are calculating the performance measures for a task, then it is the total
budget for the task.
• Planned value (PV) is the value of the work that is to be completed on the project (or,
alternatively, the work completed on any task). Since the value of the work completed is
how much effort and money will be put into it, you can think of planned value (PV) as the
budgeted cost of work scheduled.
• Actual Cost (AC) is the total cost (direct and indirect) incurred in completing the work
on the project (or, alternatively, a task) up to that particular point in time. Another way of
referring to this is actual cost of work performed to date.
• Earned value (EV) is an estimate of the value of the work performed thus far. Earned value
therefore refers to only the work that has been completed to date. We can calculate earned
value (EV) as follows:
EV 5 PV * p
where p is the percentage of the work completed thus far.
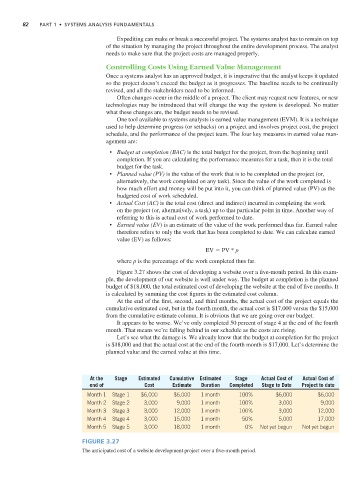
Figure 3.27 shows the cost of developing a website over a five-month period. In this exam-
ple, the development of our website is well under way. The budget at completion is the planned
budget of $18,000, the total estimated cost of developing the website at the end of five months. It
is calculated by summing the cost figures in the estimated cost column.
At the end of the first, second, and third months, the actual cost of the project equals the
cumulative estimated cost, but in the fourth month, the actual cost is $17,000 versus the $15,000
from the cumulative estimate column. It is obvious that we are going over our budget.
It appears to be worse. We’ve only completed 50 percent of stage 4 at the end of the fourth
month. That means we’re falling behind in our schedule as the costs are rising.
Let’s see what the damage is. We already know that the budget at completion for the project
is $18,000 and that the actual cost at the end of the fourth month is $17,000. Let’s determine the
planned value and the earned value at this time.
At the Stage Estimated Cumulative Estimated Stage Actual Cost of Actual Cost of
end of Cost Estimate Duration Completed Stage to Date Project to date
Month 1 Stage 1 $6,000 $6,000 1 month 100% $6,000 $6,000
Month 2 Stage 2 3,000 9,000 1 month 100% 3,000 9,000
Month 3 Stage 3 3,000 12,000 1 month 100% 3,000 12,000
Month 4 Stage 4 3,000 15,000 1 month 50% 5,000 17,000
Month 5 Stage 5 3,000 18,000 1 month 0% Not yet begun Not yet begun
Figure 3.27
The anticipated cost of a website development project over a five-month period.