Page 222 -
P. 222
chaPter 7 • Using Data Flow Diagrams 189
Logical Data Flow Diagram
Customer D1 Prices Customer
Items to Prices Payment
Purchase Receipt
1 2 3 4
Settle
Identify Item ID Look Up Items and Prices Compute Amount to Be Paid Transaction
Total
Item Prices Cost of and Issue
Order Receipt
Physical Data Flow Diagram
Customer D1 UPC Price File D2 Temporary Customer
Trans. File
Items Brought UPC Code Item Description Items and Items, Prices, Cash, Check,
Prices
to Checkout and Prices and Subtotals or Debit Card Cash Register
Receipt
1 2 3 4
Calculated
Pass UPC Bar Code Look Up Item Codes and Prices Amount to Be Paid Collect Money
Items Over Code and Compute and Give
Scanner Price Total Receipt
(Manual) in File Cost (Manual)
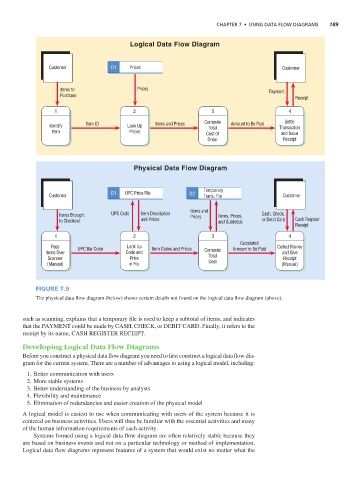
Figure 7.9
The physical data flow diagram (below) shows certain details not found on the logical data flow diagram (above).
such as scanning, explains that a temporary file is used to keep a subtotal of items, and indicates
that the PAYMENT could be made by CASH, CHECK, or DEBIT CARD. Finally, it refers to the
receipt by its name, CASH REGISTER RECEIPT.
Developing Logical Data Flow Diagrams
Before you construct a physical data flow diagram you need to first construct a logical data flow dia-
gram for the current system. There are a number of advantages to using a logical model, including:
1. Better communication with users
2. More stable systems
3. Better understanding of the business by analysts
4. Flexibility and maintenance
5. Elimination of redundancies and easier creation of the physical model
A logical model is easiest to use when communicating with users of the system because it is
centered on business activities. Users will thus be familiar with the essential activities and many
of the human information requirements of each activity.
Systems formed using a logical data flow diagram are often relatively stable because they
are based on business events and not on a particular technology or method of implementation.
Logical data flow diagrams represent features of a system that would exist no matter what the