Page 511 - Tandem Techniques
P. 511
Page 497
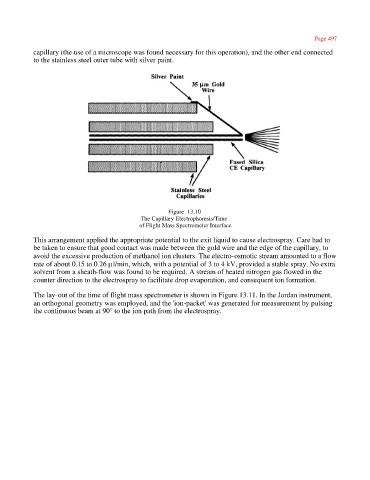
capillary (the use of a microscope was found necessary for this operation), and the other end connected
to the stainless steel outer tube with silver paint.
Figure 13.10
The Capillary Electrophoresis/Time
of Flight Mass Spectrometer Interface
This arrangement applied the appropriate potential to the exit liquid to cause electrospray. Care had to
be taken to ensure that good contact was made between the gold wire and the edge of the capillary, to
avoid the excessive production of methanol ion clusters. The electro-osmotic stream amounted to a flow
rate of about 0.15 to 0.26 µl/min, which, with a potential of 3 to 4 kV, provided a stable spray. No extra
solvent from a sheath-flow was found to be required. A stream of heated nitrogen gas flowed in the
counter direction to the electrospray to facilitate drop evaporation, and consequent ion formation.
The lay-out of the time of flight mass spectrometer is shown in Figure 13.11. In the Jordan instrument,
an orthogonal geometry was employed, and the 'ion-packet' was generated for measurement by pulsing
the continuous beam at 90° to the ion path from the electrospray.