Page 171 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 171
20:32
Char Count= 0
March 9, 2004
WU095-08
WU095/Kulaev
Yeast 155
200
4
150
3
n 100
50
2
1a
1b
10
A B C D
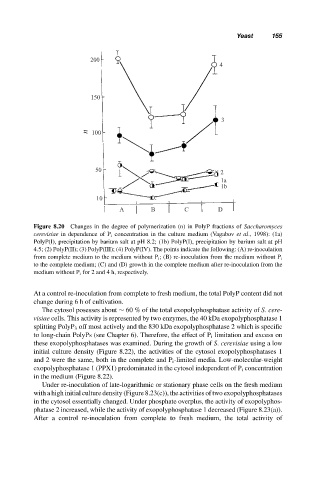
Figure 8.20 Changes in the degree of polymerization (n) in PolyP fractions of Saccharomyces
cerevisiae in dependence of P i concentration in the culture medium (Vagabov et al., 1998): (1a)
PolyP(I), precipitation by barium salt at pH 8.2; (1b) PolyP(I), precipitation by barium salt at pH
4.5; (2) PolyP(II); (3) PolyP(III); (4) PolyP(IV). The points indicate the following: (A) re-inoculation
from complete medium to the medium without P i ; (B) re-inoculation from the medium without P i
to the complete medium; (C) and (D) growth in the complete medium after re-inoculation from the
medium without P i for 2 and 4 h, respectively.
At a control re-inoculation from complete to fresh medium, the total PolyP content did not
change during 6 h of cultivation.
The cytosol posesses about ∼ 60 % of the total exopolyphosphatase activity of S. cere-
visiae cells. This activity is represented by two enzymes, the 40 kDa exopolyphosphatase 1
splitting PolyP 3 off most actively and the 830 kDa exopolyphosphatase 2 which is specific
to long-chain PolyPs (see Chapter 6). Therefore, the effect of P i limitation and excess on
these exopolyphosphatases was examined. During the growth of S. cerevisiae using a low
initial culture density (Figure 8.22), the activities of the cytosol exopolyphosphatases 1
and 2 were the same, both in the complete and P i -limited media. Low-molecular-weight
exopolyphosphatase 1 (PPX1) predominated in the cytosol independent of P i concentration
in the medium (Figure 8.22).
Under re-inoculation of late-logarithmic or stationary phase cells on the fresh medium
with a high initial culture density (Figure 8.23(c)), the activities of two exopolyphosphatases
in the cytosol essentially changed. Under phosphate overplus, the activity of exopolyphos-
phatase 2 increased, while the activity of exopolyphosphatase 1 decreased (Figure 8.23(a)).
After a control re-inoculation from complete to fresh medium, the total activity of