Page 176 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 176
WU095/Kulaev
WU095-08
Peculiarities of polyphosphate metabolism
160 March 9, 2004 20:32 Char Count= 0
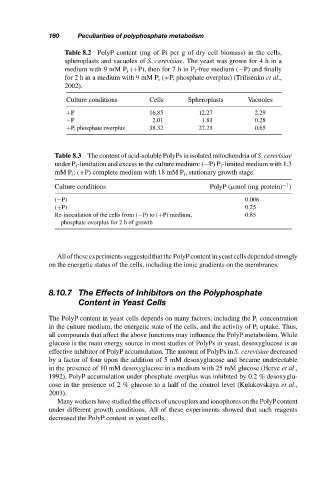
Table 8.2 PolyP content (mg of Pi per g of dry cell biomass) in the cells,
spheroplasts and vacuoles of S. cerevisiae. The yeast was grown for4hina
medium with 9 mM P i (+P), then for 7 h in P i -free medium (−P) and finally
for 2 h in a medium with 9 mM P i (+P, phosphate overplus) (Trilisenko et al.,
2002).
Culture conditions Cells Spheroplasts Vacuoles
+P 16.85 12.27 2.29
−P 2.01 1.81 0.28
+P, phosphate overplus 38.32 27.21 0.65
Table 8.3 The content of acid-soluble PolyPs in isolated mitochondria of S. cerevisiae
under P i -limitation and excess in the culture medium: (−P) P i -limited medium with 1.3
mM P i ;(+P) complete medium with 18 mM P i , stationary growth stage.
−1
Culture conditions PolyP (µmol (mg protein) )
(−P) 0.006
(+P) 0.25
Re-inoculation of the cells from (−P) to (+P) medium, 0.85
phosphate overplus for2hofgrowth
All of these experiments suggested that the PolyP content in yeast cells depended strongly
on the energetic status of the cells, including the ionic gradients on the membranes.
8.10.7 The Effects of Inhibitors on the Polyphosphate
Content in Yeast Cells
The PolyP content in yeast cells depends on many factors, including the P i concentration
in the culture medium, the energetic state of the cells, and the activity of P i uptake. Thus,
all compounds that affect the above functions may influence the PolyP metabolism. While
glucose is the main energy source in most studies of PolyPs in yeast, desoxyglucose is an
effective inhibitor of PolyP accumulation. The amount of PolyPs in S. cerevisiae decreased
by a factor of four upon the addition of 5 mM desoxyglucose and became undetectable
in the presence of 10 mM desoxyglucose in a medium with 25 mM glucose (Herve et al.,
1992). PolyP accumulation under phosphate overplus was inhibited by 0.2 % desoxyglu-
cose in the presence of 2 % glucose to a half of the control level (Kulakovskaya et al.,
2003).
Many workers have studied the effects of uncouplers and ionophores on the PolyP content
under different growth conditions. All of these experiments showed that such reagents
decreased the PolyP content in yeast cells.