Page 175 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 175
20:32
Char Count= 0
March 9, 2004
WU095-08
WU095/Kulaev
Yeast 159
400
PolyP ( µmol P (g dry biomass) −1 ) 300
200
100
0
12345 12345 12345 12345 12345 12345 12345
A B C D E F G
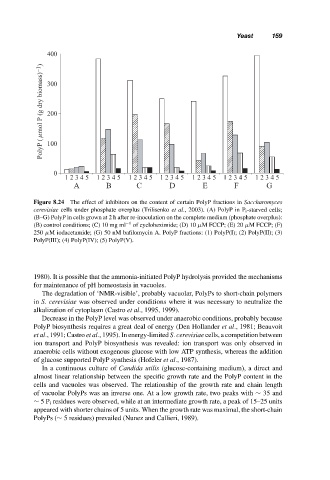
Figure 8.24 The effect of inhibitors on the content of certain PolyP fractions in Saccharomyces
cerevisiae cells under phosphate overplus (Trilisenko et al., 2003). (A) PolyP in P i -starved cells;
(B–G) PolyP in cells grown at 2 h after re-inoculation on the complete medium (phosphate overplus):
(B) control conditions; (C) 10 mg ml −1 of cycloheximide; (D) 10 µM FCCP; (E) 20 µM FCCP; (F)
250 µM iodacetamide; (G) 50 nM bafilomycin A. PolyP fractions: (1) PolyP(I); (2) PolyP(II); (3)
PolyP(III); (4) PolyP(IV); (5) PolyP(V).
1980). It is possible that the ammonia-initiated PolyP hydrolysis provided the mechanisms
for maintenance of pH homeostasis in vacuoles.
The degradation of ‘NMR-visible’, probably vacuolar, PolyPs to short-chain polymers
in S. cerevisiae was observed under conditions where it was necessary to neutralize the
alkalization of cytoplasm (Castro et al., 1995, 1999).
Decrease in the PolyP level was observed under anaerobic conditions, probably because
PolyP biosynthesis requires a great deal of energy (Den Hollander et al., 1981; Beauvoit
et al., 1991; Castro et al., 1995). In energy-limited S. cerevisiae cells, a competition between
ion transport and PolyP biosynthesis was revealed: ion transport was only observed in
anaerobic cells without exogenous glucose with low ATP synthesis, whereas the addition
of glucose supported PolyP synthesis (Hofeler et al., 1987).
In a continuous culture of Candida utilis (glucose-containing medium), a direct and
almost linear relationship between the specific growth rate and the PolyP content in the
cells and vacuoles was observed. The relationship of the growth rate and chain length
of vacuolar PolyPs was an inverse one. At a low growth rate, two peaks with ∼ 35 and
∼ 5P i residues were observed, while at an intermediate growth rate, a peak of 15–25 units
appeared with shorter chains of 5 units. When the growth rate was maximal, the short-chain
PolyPs (∼ 5 residues) prevailed (Nunez and Callieri, 1989).