Page 216 - The Combined Finite-Discrete Element Method
P. 216
DYNAMICS OF IRREGULAR DISCRETE ELEMENTS SUBJECT 199
Numerical solution
Analytical solution
1
Angular velocity (1/s) −0.5 0
0.5
−1
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25
Time (s)
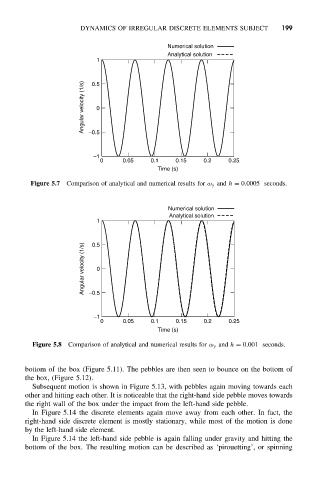
Figure 5.7 Comparison of analytical and numerical results for ω y and h = 0.0005 seconds.
Numerical solution
Analytical solution
1
0.5
Angular velocity (1/s) −0.5 0
−1
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25
Time (s)
Figure 5.8 Comparison of analytical and numerical results for ω y and h = 0.001 seconds.
bottom of the box (Figure 5.11). The pebbles are then seen to bounce on the bottom of
the box, (Figure 5.12).
Subsequent motion is shown in Figure 5.13, with pebbles again moving towards each
other and hitting each other. It is noticeable that the right-hand side pebble moves towards
the right wall of the box under the impact from the left-hand side pebble.
In Figure 5.14 the discrete elements again move away from each other. In fact, the
right-hand side discrete element is mostly stationary, while most of the motion is done
by the left-hand side element.
In Figure 5.14 the left-hand side pebble is again falling under gravity and hitting the
bottom of the box. The resulting motion can be described as ‘pirouetting’, or spinning