Page 41 - The Combined Finite-Discrete Element Method
P. 41
24 INTRODUCTION
(a) (b) (c)
(d) (e) (f)
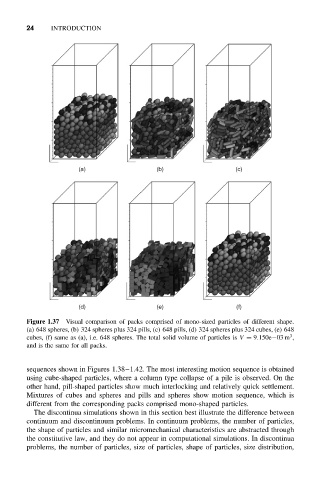
Figure 1.37 Visual comparison of packs comprised of mono-sized particles of different shape.
(a) 648 spheres, (b) 324 spheres plus 324 pills, (c) 648 pills, (d) 324 spheres plus 324 cubes, (e) 648
3
cubes, (f) same as (a), i.e. 648 spheres. The total solid volume of particles is V = 9.150e−03 m ,
and is the same for all packs.
sequences shown in Figures 1.38–1.42. The most interesting motion sequence is obtained
using cube-shaped particles, where a column type collapse of a pile is observed. On the
other hand, pill-shaped particles show much interlocking and relatively quick settlement.
Mixtures of cubes and spheres and pills and spheres show motion sequence, which is
different from the corresponding packs comprised mono-shaped particles.
The discontinua simulations shown in this section best illustrate the difference between
continuum and discontinuum problems. In continuum problems, the number of particles,
the shape of particles and similar micromechanical characteristics are abstracted through
the constitutive law, and they do not appear in computational simulations. In discontinua
problems, the number of particles, size of particles, shape of particles, size distribution,