Page 376 - Bruce Ellig - The Complete Guide to Executive Compensation (2007)
P. 376
362 The Complete Guide to Executive Compensation
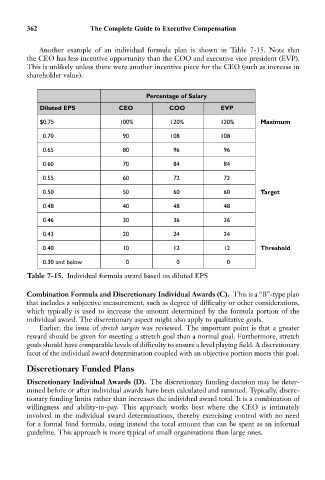
Another example of an individual formula plan is shown in Table 7-15. Note that
the CEO has less incentive opportunity than the COO and executive vice president (EVP).
This is unlikely unless there were another incentive piece for the CEO (such as increase in
shareholder value).
Percentage of Salary
Diluted EPS CEO COO EVP
$0.75 100% 120% 120% Maximum
0.70 90 108 108
0.65 80 96 96
0.60 70 84 84
0.55 60 72 72
0.50 50 60 60 Target
0.48 40 48 48
0.46 30 36 36
0.43 20 24 24
0.40 10 12 12 Threshold
0.30 and below 0 0 0
Table 7-15. Individual formula award based on diluted EPS
Combination Formula and Discretionary Individual Awards (C). This is a “B”-type plan
that includes a subjective measurement, such as degree of difficulty or other considerations,
which typically is used to increase the amount determined by the formula portion of the
individual award. The discretionary aspect might also apply to qualitative goals.
Earlier, the issue of stretch targets was reviewed. The important point is that a greater
reward should be given for meeting a stretch goal than a normal goal. Furthermore, stretch
goals should have comparable levels of difficulty to ensure a level playing field. A discretionary
facet of the individual award determination coupled with an objective portion meets this goal.
Discretionary Funded Plans
Discretionary Individual Awards (D). The discretionary funding decision may be deter-
mined before or after individual awards have been calculated and summed. Typically, discre-
tionary funding limits rather than increases the individual award total. It is a combination of
willingness and ability-to-pay. This approach works best where the CEO is intimately
involved in the individual award determinations, thereby exercising control with no need
for a formal fund formula, using instead the total amount that can be spent as an informal
guideline. This approach is more typical of small organizations than large ones.