Page 274 - The Handbook for Quality Management a Complete Guide to Operational Excellence
P. 274
260 C o n t i n u o u s I m p r o v e m e n t e f f e c t i v e C h a n g e M a n a g e m e n t 261
type of project to focus on; that is, should we focus on quality, cost, or
schedule projects? Assume that you have three Six Sigma candidate proj-
ects, all focusing on process step B, the constraint. The area addressed is
correct, but which project should you pursue first? Let’s assume that we
learn that one project will primarily improve quality, another cost, and
another schedule. Does this new information help? Definitely! Take a look
at Table 12.4 to see how this information can be used. Projects in the same
priority group are ranked according to their impact on throughput.
The same thought process can be applied to process steps before and
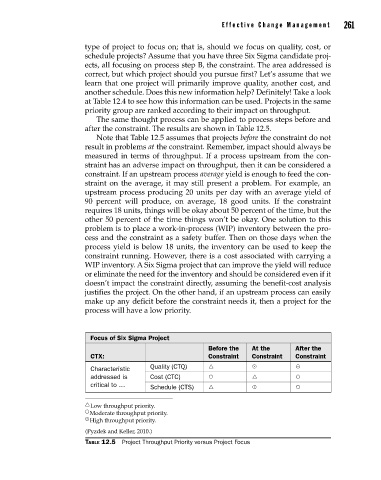
after the constraint. The results are shown in Table 12.5.
Note that Table 12.5 assumes that projects before the constraint do not
result in problems at the constraint. Remember, impact should always be
measured in terms of throughput. If a process upstream from the con-
straint has an adverse impact on throughput, then it can be considered a
constraint. If an upstream process average yield is enough to feed the con-
straint on the average, it may still present a problem. For example, an
upstream process producing 20 units per day with an average yield of
90 percent will produce, on average, 18 good units. If the constraint
requires 18 units, things will be okay about 50 percent of the time, but the
other 50 percent of the time things won’t be okay. One solution to this
problem is to place a work-in-process (WIP) inventory between the pro-
cess and the constraint as a safety buffer. Then on those days when the
process yield is below 18 units, the inventory can be used to keep the
constraint running. However, there is a cost associated with carrying a
WIP inventory. A Six Sigma project that can improve the yield will reduce
or eliminate the need for the inventory and should be considered even if it
doesn’t impact the constraint directly, assuming the benefit-cost analysis
justifies the project. On the other hand, if an upstream process can easily
make up any deficit before the constraint needs it, then a project for the
process will have a low priority.
Focus of Six Sigma Project
Before the At the After the
CTX: Constraint Constraint Constraint
Characteristic Quality (CTQ) ^ } }
addressed is Cost (CTC) ~ ^ ~
critical to … Schedule (CTS) ^ } ~
^ Low throughput priority.
~ Moderate throughput priority.
} High throughput priority.
(Pyzdek and Keller, 2010.)
Table 12.5 Project Throughput Priority versus Project Focus
12_Pyzdek_Ch12_p241-264.indd 261 11/9/12 5:13 PM