Page 19 - The Petroleum System From Source to Trap
P. 19
1. The Petroleum System 11
1
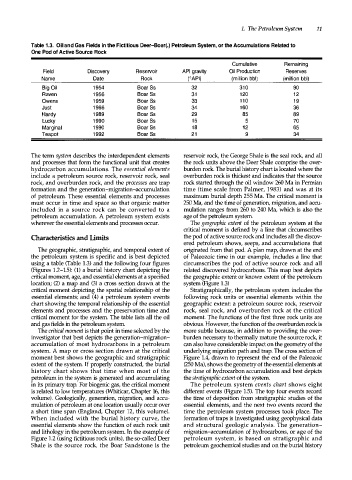
Table . 3. Oil and Gas Fields in the Fictitious Deer-Boar(.) Petroleum System, or the Accumulations Related to
One Pod of Active Source Rock
Cumulative Remaining
Field Discovery Reservoir API gravity Oil Production Reserves
Name Date Rock (0API) (million bbl) (million bbl)
Big Oil 1 9 54 Boar Ss 32 31 0 90
Raven 1 9 56 Boar Ss 31 1 2 0 1 2
Owens 1 9 59 Boar Ss 33 1 1 0 1 9
Just 1 9 66 Boar Ss 34 1 6 0 36
Hardy 1 9 89 Boar Ss 29 85 89
Lucky 1 9 90 Boar Ss 1 5 5 70
Marginal 1 9 90 Boar Ss 1 8 12 65
Teapot 1 9 92 Boar Ss 21 9 34
The term system describes the interdependent elements reservoir rock, the George Shale is the seal rock, and all
and processes that form the functional unit that creates the rock units above the Deer Shale comprise the over
hydrocarbon accumulations. The essential elements burden rock The burial history chart is located where the
include a petroleum source rock, reservoir rock, seal overburden rock is thickest and indicates that the source
rock, and overburden rock, and the processes are trap rock started through the oil window 260 Ma in Permian
formation and the generation-migration-accumulation time (time scale from Palmer, 1 9 83) and was at its
of petroleum. These essential elements and processes maximum burial depth 255 Ma. The critical moment is
must occur in time and space so that organic matter 250 Ma, and the time of generation, migration, and accu
included in a source rock can be converted to a mulation ranges from 260 to 240 Ma, which is also the
petroleum accumulation. A petroleum system exists age of the petroleum system.
wherever the essential elements and processes occur. The geographic extent of the petroleum system at the
critical moment is defined by a line that circumscribes
Characteristics and Limits the pod of active source rock and includes all the discov
ered petroleum shows, seeps, and accumulations that
The geographic, stratigraphic, and temporal extent of originated from that pod. A plan map, drawn at the end
the petroleum system is specific and is best depicted of Paleozoic time in our example, includes a line that
using a table (Table 1.3) and the following four figures circumscribes the pod of active source rock and all
(Figures 1 . 2-1.5): (1) a burial history chart depicting the related discovered hydrocarbons. This map best depicts
critical moment, age, and essential elements at a specified the geographic extent or known extent of the petroleum
location; (2) a map and (3) a cross section drawn at the system (Figure . 3)
1
critical moment depicting the spatial relationship of the Stratigraphically, the petroleum system includes the
essential elements; and (4) a petroleum system events following rock units or essential elements within the
chart showing the temporal relationship of the essential geographic extent: a petroleum source rock, reservoir
elements and processes and the preservation time and rock, seal rock, and overburden rock at the critical
critical moment for the system. The table lists all the oil moment. The functions of the first three rock units are
and gas fields in the petroleum system. obvious. However, the function of the overburden rock is
The critical moment is that point in time selected by the more subtle because, in addition to providing the over
investigator that best depicts the generation-migration burden necessary to thermally mature the source rock, it
accumulation of most hydrocarbons in a petroleum can also have considerable impact on the geometry of the
system. A map or cross section drawn at the critical underlying migration path and trap. The cross section of
moment best shows the geographic and stratigraphic Figure 1.4, drawn to represent the end of the Paleozoic
extent of the system. If properly constructed, the burial (250 Ma), shows the geometry of the essential elements at
history chart shows that time when most of the the time of hydrocarbon accumulation and best depicts
petroleum in the system is generated and accumulating the stratigraphic extent of the system.
in its primary trap. For biogenic gas, the critical moment The petroleum system events chart shows eight
is related to low temperatures (Whiticar, Chapter 16, this different events (Figure 1 . 5). The top four events record
volume). Geologically, generation, migration, and accu the time of deposition from stratigraphic studies of the
mulation of petroleum at one location usually occur over essential elements, and the next two events record the
a short time span (England, Chapter 12, this volume). time the petroleum system processes took place. The
When included with the burial history curve, the formation of traps is investigated using geophysical data
essential elements show the function of each rock unit and structural geologic analysis. The generation
and lithology in the petroleum system. In the example of migration-accumulation of hydrocarbons, or age of the
Figure 1.2 (using fictitious rock units), the so-called Deer petroleum system, is based on stratigraphic and
Shale is the source rock, the Boar Sandstone is the petroleum geochemical studies and on the burial history