Page 21 - The Petroleum System From Source to Trap
P. 21
1. The Petroleum System 13
, .
<·:;·:::-:<·:::;-;:_\�.'.·._ �:·: : ::>::::: · ' .
· ?'L.i(:�f;ii�
Ma
� Line of cross section • • • Top oil window
...A.....��- Thrust be� sawteeth on upper plate � � o Top gas window
....L......L.- Fau� hatchures on downthrown block --i> Direction of petroleum migration
.. Petroleum accumulation
Plunging anticline
Plunging syncline l h !:ut�l Source rock
* Location used for burial history chart v·�;_i·:·(:�� Reservoir rock
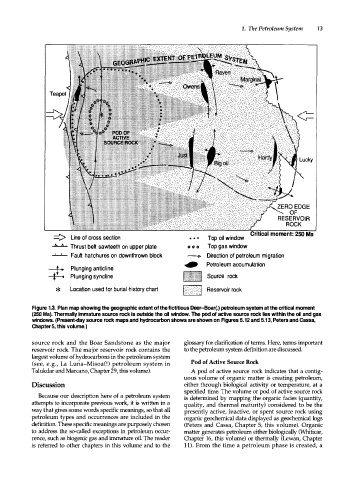
Figure 1.3. Plan map showing the geographic extent of the fictitious Deer-Boar(.) petroleum system at the critical moment
(250 Ma). Thermally immature source rock is outside the oil window. The pod of active source rock lies within the oil and gas
windows. (Present-day source rock maps and hydrocarbon shows are shown on Figures 5.12 and 5. 3 , Peters and Cassa,
1
Chapter 5, this volume.)
source rock and the Boar Sandstone as the major glossary for clarification of terms. Here, terms important
reservoir rock. The major reservoir rock contains the to the petroleum system definition are discussed.
largest volume of hydrocarbons in the petroleum system
(see, e.g., La Luna-Misoa(!) petroleum system in Pod of Active Source Rock
Talukdar and Marcano, Chapter 29, this volume). A pod of active source rock indicates that a contig
uous volume of organic matter is creating petroleum,
Discussion either through biological activity or temperature, at a
specified time. The volume or pod of active source rock
Because our description here of a petroleum system is determined by mapping the organic facies (quantity,
attempts to incorporate previous work, it is written in a quality, and thermal maturity) considered to be the
way that gives some words specific meanings, so that all presently active, inactive, or spent source rock using
petroleum types and occurrences are included in the organic geochemical data displayed as geochemical logs
definition. These specific meanings are purposely chosen (Peters and Cassa, Chapter 5, this volume). Organic
to address the so-called exceptions in petroleum occur matter generates petroleum either biologically (Whiticar,
rence, such as biogenic gas and immature oil. The reader Chapter 16, this volume) or thermally (Lewan, Chapter
is referred to other chapters in this volume and to the 1 1 ) . From the time a petroleum phase is created, a