Page 23 - The Petroleum System From Source to Trap
P. 23
1. The Petroleum System 15
1
400 300 200 1 0 0 Table . 4. Definitions of Levels of Certainty
e
PALEOZOIC MESOZOIC �ENOZOIC g � Level of
m
o i M I IP I P li l j I K I P, IN s Certainty Symbol Criteria
� Source Rock Known (!) Oil-source rock or gas-source
·
I . >.:..] Reservoir Rock rock correlation
I Seal Rock Hypothetical ( .) In absence of petroleum-source
rock correlation, geochemical
I Overburden Rock evidence indicates the origin of
Trap Formation the oil and gas
I Generation-Migration- : Speculative (?) Geologic or geophysical
Accumulation
.. . . Preservation Time evidence
t Critical Moment
Preservation Time
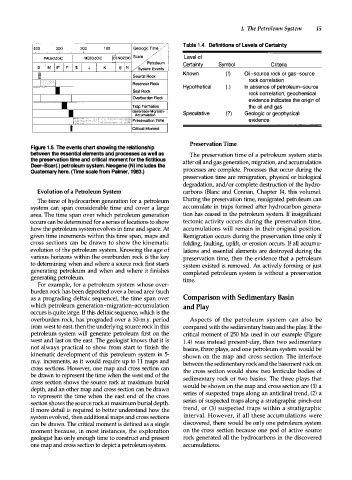
Figure . 5. The events chart showing the relationship
1
between the essential elements and processes as well as The preservation time of a petroleum system starts
the preservation time and critical moment for the fictitious after oil and gas generation, migration, and accumulation
Deer-Boar(.) petroleum system. Neogene (N) includes the
Quaternary here. (Time scale from Palmer, 1983.) processes are complete. Processes that occur during the
preservation time are remigration, physical or biological
degradation, and/ or complete destruction of the hydro
Evolution of a Petroleum System carbons (Blanc and Connan, Chapter 14, this volume).
The time of hydrocarbon generation for a petroleum During the preservation time, remigrated petroleum can
system can span considerable time and cover a large accumulate in traps formed after hydrocarbon genera
area. The time span over which petroleum generation tion has ceased in the petroleum system. If insignificant
occurs can be determined for a series of locations to show tectonic activity occurs during the preservation time,
how the petroleum system evolves in time and space. At accumulations will remain in their original position.
given time increments within this time span, maps and Remigration occurs during the preservation time only if
cross sections can be drawn to show the kinematic folding, faulting, uplift, or erosion occurs. If all accumu
evolution of the petroleum system. Knowing the age of lations and essential elements are destroyed during the
various horizons within the overburden rock is the key preservation time, then the evidence that a petroleum
to determing when and where a source rock first starts system existed is removed. An actively forming or just
generating petroleum and when and where it finishes completed petroleum system is without a preservation
generating petroleum. time.
For example, for a petroleum system whose over
burden rock has been deposited over a broad area (such
as a prograding deltaic sequence), the time span over Comparison with Sedimentary Basin
which petroleum generation-migration-accumulation and Play
occurs is quite large. If this deltaic sequence, which is the
overburden rock, has prograded over a 50-m.y. period Aspects of the petroleum system can also be
from west to east, then the underlying source rock in this compared with the sedimentary basin and the play. If the
petroleum system will generate petroleum first on the critical moment of 250 Ma used in our example (Figure
west and last on the east. The geologist knows that it is 1 . 4) was instead present-day, then two sedimentary
not always practical to show from start to finish the basins, three plays, and one petroleum system would be
kinematic development of this petroleum system in 5- shown on the map and cross section. The interface
m.y. increments, as it would require up to 1 1 maps and between the sedimentary rock and the basement rock on
cross sections. However, one map and cross section can the cross section would show two lenticular bodies of
be drawn to represent the time when the west end of the sedimentary rock or two basins. The three plays that
cross section shows the source rock at maximum burial
depth, and an other map and cross section can be drawn would be shown on the map and cross section are (1) a
to represent the time when the east end of the cross series of suspected traps along an anticlinal trend, (2) a
section shows the source rock at maximum burial depth. series of suspected traps along a stratigraphic pinch-out
If more detail is required to better understand how the trend, or (3) suspected traps within a stratigraphic
system evolved, then additional maps and cross sections interval. However, if all these accumulations were
can be drawn. The critical moment is defined as a single discovered, there would be only one petroleum system
moment because, in most instances, the exploration on the cross section because one pod of active source
geologist has only enough time to construct and present rock generated all the hydrocarbons in the discovered
one map and cross section to depict a petroleum system. accumulations.