Page 22 - The Petroleum System From Source to Trap
P. 22
14 Magoon and Dow
1-j----- GEOGRAPHIC EXTENT OF PETROLEUM SYSTEM
A A
I I
STRATIGRAPHIC \ , ' , I ,
EXTENT OF ' ... : \ .. ' - , .-
,
_____ ..._. , ..
PETROLEUM 1 t � I _ .., ...
SYSTEM - " I , •
• . . . . . . . ' ... ... .:: ,-
·. . . . Overburden rock
' ... .. _, ...
I - ; -- , - Essential
, '
:: - I elements Seal rock
of Sedimentary
petroleum Reservoir rock basin fill
POD OF ACTIVE system Source rock
SOURCE ROCK
- Petroleum accu m u lation (A) Underburden rock
I Fold-and-thrust belt: arrows � Basement rock
indicate direction of relative motion
• • • Top oil window
* Location used for burial history chart
� � � Top gas window
Critical moment: 250 Ma
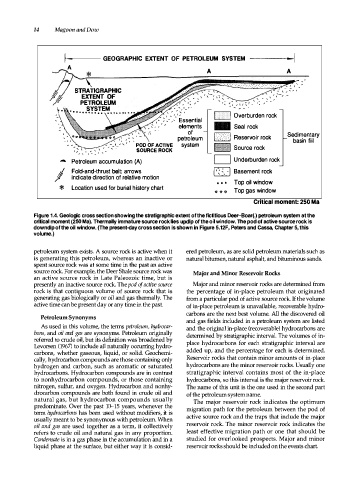
Figure 1.4. Geologic cross section showing the stratigraphic extent of the fictitious Deer-Boar(.) petroleum system at the
critical moment (250 Ma). Thermally immature source rock lies updip of the oil window. The pod of active source rock is
downdip of the oil window. (The present-day cross section is shown in Figure 5.12F, Peters and Cassa, Chapter 5, this
volume.)
petroleum system exists. A source rock is active when it ered petroleum, as are solid petroleum materials such as
is generating this petroleum, whereas an inactive or natural bitumen, natural asphalt, and bituminous sands.
spent source rock was at some time in the past an active
source rock. For example, the Deer Shale source rock was Major and Minor Reservoir Rocks
an active source rock in Late Paleozoic time, but is
presently an inactive source rock. The pod o f active source Major and minor reservoir rocks are determined from
rock is that contiguous volume of source rock that is the percentage of in-place petroleum that originated
generating gas biologically or oil and gas thermally. The from a particular pod of active source rock. If the volume
active time can be present day or any time in the past. of in-place petroleum is unavailable, recoverable hydro
carbons are the next best volume. All the discovered oil
Petroleum Synonyms
and gas fields included in a petroleum system are listed
As used in this volume, the terms petroleum, hydrocar and the original in-place (recoverable) hydrocarbons are
bons, and oil and gas are synonyms. Petroleum originally determined by stratigraphic interval. The volumes of in
referred to crude oil, but its definition was broadened by
Levorsen (1967) to include all naturally occurring hydro place hydrocarbons for each stratigraphic interval are
carbons, whether gaseous, liquid, or solid. Geochemi added up, and the percentage for each is determined.
cally, hydrocarbon compounds are those containing only Reservoir rocks that contain minor amounts of in-place
hydrogen and carbon, such as aromatic or saturated hydrocarbons are the minor reservoir rocks. Usually one
hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbon compounds are in contrast stratigraphic interval contains most of the in-place
to nonhydrocarbon compounds, or those containing hydrocarbons, so this interval is the major reservoir rock.
nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen. Hydrocarbon and nonhy The name of this unit is the one used in the second part
drocarbon compounds are both found in crude oil and of the petroleum system name.
natural gas, but hydrocarbon compounds usually The major reservoir rock indicates the optimum
predominate. Over the past 10-15 years, whenever the migration path for the petroleum between the pod of
term hydrocarbons has been used without modifiers, it is
usually meant to be synonymous with petroleum. When active source rock and the traps that include the major
oil and gas are used together as a term, it collectively reservoir rock. The minor reservoir rock indicates the
refers to crude oil and natural gas in any proportion. least effective migration path or one that should be
Condensate is in a gas phase in the accumulation and in a studied for overlooked prospects. Major and minor
liquid phase at the surface, but either way it is consid- reservoir rocks should be included on the events chart.