Page 35 - The Petroleum System From Source to Trap
P. 35
2. Petroleum System Logic as an E xp loration Tool 27
0
1- 5
u. (.)
� w
(/)
:r I
1- w 2
fu 1 0 :::E
0 i=
3
15
4 i.:.:.:.:.:�:·:·:,J SAND
c=J SHALE
TOP PLIOCENE
M-2 10 MILES
M-11
M-13
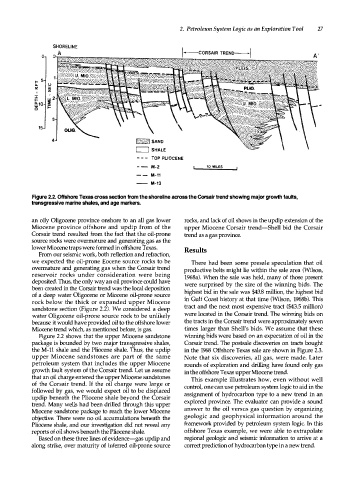
Figure 2.2. Offshore Texas cross section from the shoreline across the Corsair trend showing major growth faults,
transgressive marine shales, and age markers.
an oily Oligocene province onshore to an all gas lower rocks, and lack of oil shows in the updip extension of the
Miocene province offshore and updip from of the upper Miocene Corsair trend-Shell bid the Corsair
Corsair trend resulted from the fact that the oil-prone trend as a gas province.
source rocks were overmature and generating gas as the
lower Miocene traps were formed in offshore Texas. Results
From our seismic work, both reflection and refraction,
we expected the oil-prone Eocene source rocks to be There had been some presale speculation that oil
overmature and generating gas when the Corsair trend productive belts might lie within the sale area (Wilson,
reservoir rocks under consideration were being 1968a). When the sale was held, many of those present
deposited. Thus, the only way an oil province could have were surprised by the size of the winning bids. The
been created in the Corsair trend was the local deposition
of a deep water Oligocene or Miocene oil-prone source highest bid in the sale was $43.8 million, the highest bid
rock below the thick or expanded upper Miocene in Gulf Coast history at that time (Wilson, 1968b). This
sandstone section (Figure 2.2). We considered a deep tract and the next most expensive tract ($43.5 million)
water Oligocene oil-prone source rock to be unlikely were located in the Corsair trend. The winning bids on
because it would have provided oil to the offshore lower the tracts in the Corsair trend were approximately seven
Miocene trend which, as mentioned before, is gas. times larger than Shell's bids. We assume that these
Figure 2.2 shows that the upper Miocene sandstone winning bids were based on an expectation of oil in the
package is bounded by two major transgressive shales, Corsair trend. The postsale discoveries on tracts bought
the M-11 shale and the Pliocene shale. Thus, the updip in the 1968 Offshore Texas sale are shown in Figure 2.3.
upper Miocene sandstones are part of the same Note that six discoveries, all gas, were made. Later
petroleum system that includes the upper Miocene rounds of exploration and drilling have found only gas
growth fault system of the Corsair trend. Let us assume in the offshore Texas upper Miocene trend.
that an oil charge entered the upper Miocene sandstones This example illustrates how, even without well
of the Corsair trend. If the oil charge were large or control, one can use petroleum system logic to aid in the
followed by gas, we would expect oil to be displaced assignment of hydrocarbon type to a new trend in an
updip beneath the Pliocene shale beyond the Corsair
trend. Many wells had been drilled through this upper explored province. The evaluator can provide a sound
Miocene sandstone package to reach the lower Miocene answer to the oil versus gas question by organizing
objective. There were no oil accumulations beneath the geologic and geophysical information around the
Pliocene shale, and our investigation did not reveal any framework provided by petroleum system logic. In this
reports of oil shows beneath the Pliocene shale. offshore Texas example, we were able to extrapolate
Based on these three lines of evidence-gas updip and regional geologic and seismic information to arrive at a
along strike, over maturity of inferred oil-prone source correct prediction of hydrocarbon type in a new trend.