Page 80 - The Six Sigma Project Planner
P. 80
In the earlier example, the calculations assumed that the task durations could be
modeled using the beta distribution. If, during the historical analysis phase, we located
sufficient data on similar tasks, we would not have needed to make this assumption.
Instead, we could use software to determine the best-fit statistical distribution for each
task. However, if historical data are not available, we can still use CB to model our
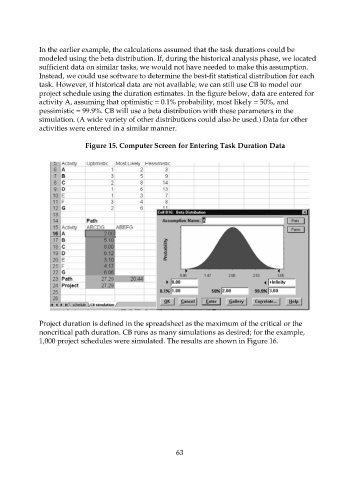
project schedule using the duration estimates. In the figure below, data are entered for
activity A, assuming that optimistic = 0.1% probability, most likely = 50%, and
pessimistic = 99.9%. CB will use a beta distribution with these parameters in the
simulation. (A wide variety of other distributions could also be used.) Data for other
activities were entered in a similar manner.
Figure 15. Computer Screen for Entering Task Duration Data
Project duration is defined in the spreadsheet as the maximum of the critical or the
noncritical path duration. CB runs as many simulations as desired; for the example,
1,000 project schedules were simulated. The results are shown in Figure 16.
63