Page 174 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 174
B3 Gears
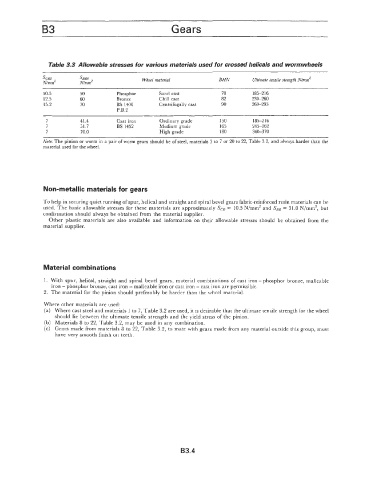
Table 3.3 Allowable stresses for various materials used for crossed helicals and wormwheels
scoz sB02 Wheel material BHN Ultimate tensile strength N/mm2
N/mmz N/mm2
10.5 50 Phosphor Sand cast 70 185-2 16
12.5 60 Bronze Chill cast 82 23G260
15.2 70 BS 1400 Centrifugally cast 90 26G293
P.B.2
7 41.4 Cast iron Ordinary grade 150 185216
7 51.7 BS 1452 Medium grade 165 245-262
7 70.0 High grade 180 34G370
Note: The pinion or worm in a pair of worm gears should be of steel, materials 3 to 7 or 20 to 22, Table 3.2, and always harder than the
material used for the wheel.
Non-metallic materials for gears
To help in securing quiet running of spur, helical and straight and spiral bevel gears fabric-reinforced resin materials can be
used. The basic allowable stresses for these materials are approximately Sc0 = 10.5 N/mm2 and S,, = 31.0 N/mm2, but
confirmation should always be obtained from the material supplier.
Other plastic materials are also available and information on their allowable stresses should be obtained from the
material supplier.
Material combinations
1. With spur, helical, straight and spiral bevel gears, material combinations of cast iron - phosphor bronze, malleable
iron -phosphor bronze, cast iron - malleable iron or cast iron - cast iron are permissible.
2. The material for the pinion should preferably be harder than the wheel material.
Where other materials are used:
(a) Where cast steel and materials 1 to 7, Table 3.2 are used, it is desirable that the ultimate tensile strength for the wheel
should lie between the ultimate tensile strength and the yield stress of the pinion.
(b) Materials 8 to 22, Table 3.2, may be used in any combination.
(c) Gears made from materials 8 to 22, Table 3.2, to mate with gears made from any material outside this group, must
have very smooth finish on teeth.
B3.4