Page 171 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 171
Gears B3
GEAR TYPES
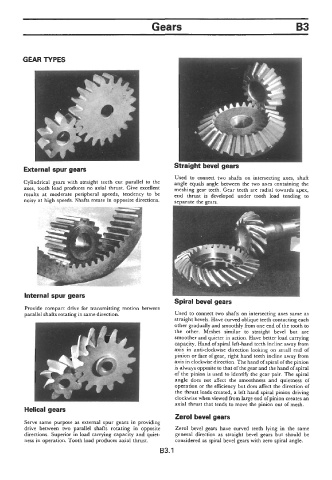
C aight bevel gears
External spur gears
Used to connect two shafts on intersecting axes, shaft
Cylindrical gears with straight teeth cut parallel to the angle equals angle between the two axes containing the
axes, tooth load produces no axial thrust. Give excellent meshing gear teeth. Gear teeth are radial towards apex,
results at moderate peripheral speeds, tendency to be end thrust is developed under tooth load tending to
noisy at high speeds. Shafts rotate in opposite directions. separate the gears.
Internal spur gears
Spiral bevel gears
Provide compact drive for transmitting motion between
parallel shafts rotating in same direction. Used to connect two shafts on intersecting axes same as
straight bevels. Have curved oblique teeth contacting each
other gradually and smoothly from one end of the tooth to
the other. Meshes similar to straight bevel but are
smoother and quieter in action. Have better load carrying
capacity. Hand of spiral left-hand teeth incline away from
axis in anti-clockwise direction looking on small end of
pinion or face of gear, right hand teeth incline away from
axis in clockwise direction. The hand of spiral of the pinion
is always opposite to that of the gear and the hand of spiral
of the pinion is used to identify the gear pair. The spiral
angle does not affect the smoothness and quietness of
operation or the efficiency but does affect the direction of
the thrust loads created, a left hand spiral pinion driving
clockwise when viewed from large end of pinion creates an
axial thrust that tends to move the pinion out of mesh.
Helical gears
Zerol bevel gears
Serve same purpose as external spur gears in providing
drive between two parallel shafts rotating in opposite Zerol bevel gears have curved teeth lying in the same
directions. Superior in load carrying capacity and quiet- general direction as straight bevel gears but should be
ness in operation. Tooth load produces axial thrust. considered as spiral bevel gears with zero spiral angle.
B3.1