Page 227 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 227
B13 Wire ropes
SELECTION OF LOAD CARRYING WIRE ROPES
Table 73.7 Ropes for industrial applications
Application Conveyors, small Excavators (drag), Lifts,* drilling Crane hoists Tower cranes Deck cranes
hoists, small lifts,* sidelines lines, scrapers, (multi-fall), (hoist), mobile (single fall),
stays, trawl (dredging), trip ropes, skip grabs, slings cranes (small), mobile cranes
warps* mast stays, hoists, pile drop ball (large)
pendants, crane driving cranes, boatfalls
ropes (small)
Construction 6 X 7(6/1) 6 X 19(9/9/1) 6 X 19 6 X 36 17 X 7(6/1) 12 X 6 over
IWRC IWRC (12/6 + 6F/l) (14/7 and 7/7/1) FC 3 X 24
IWRC IWRC
____~ ~
MBL kN 8 X 0.633 d X 0.632 d X 0.643 d X 0.630 d X 0.562 d X 0.530
Wt kg/100 m d2 X 0.382 d X 0.398 d X 0.408 8 X 0.406 d X 0.372 8 X 0.362
E N/mm2 68600 64 700 64 700 64 700 53 900 53 900
d = nominal diameter of rope Notes: Minimum Breaking Loads based on a tensile strength of 1.8 kN/mm2
FC = Fibre Core
E = Modulus of Elasticity of the rope (differs With Fibre Cores: Reduce MBL by 8% approximately.
from elastic modulus of wires in rope due to Reduce weight by 9% approximately.
helical formation of latter)
MBL = Minimum Breaking Load
IWRC = Independent Wire Rope Core
* These applications have
Fibre Main Cores
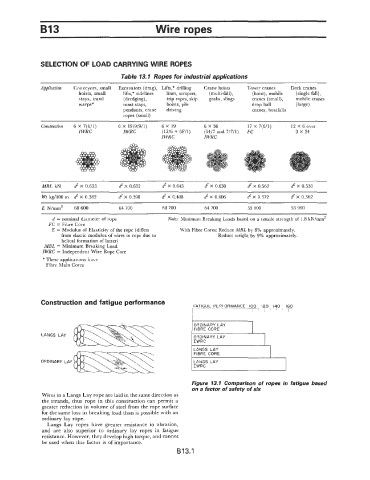
Construction and fatigue performance
FATIGUE PERFORMANCE 100, 120, 140, 160
r- 1 T
ORDINARY LAY
FIBRE CORE
LANGS LAY ORDINARY LAY
ILANGS
LAY
FIBRE CORE I
ORDINARY LAY LANGS LAY
IWRC
Figure 13.1 Comparison of ropes in fatigue based
on a factor of safety of six
Wires in a Langs Lay rope are laid in the same direction as
the strands, thus rope in this construction can permit a
greater reduction in volume of steel from the rope surface
for the same loss in breaking load than is possible with an
ordinary lay rope.
Langs Lay ropes have greater resistance to abrasion,
and are also superior to ordinary lay ropes in fatigue
resistance. However, they develop high torque, and cannot
be used when this factor is of importance.
613.1