Page 87 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 87
A14 Spherical bearings
Selection of ball joints
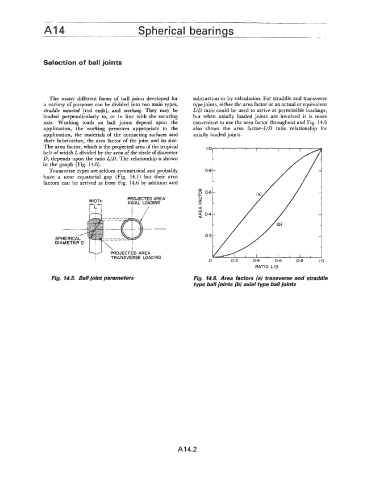
The many different forms of ball joints developed for subtraction or by calculation. For straddle and transverse
a variety of purposes can be divided into two main types, type joints, either the area factor or an actual or equivalent
straddle mounted [rod ends], and overhung. They may be WD ratio could be used to arrive at permissible loadings,
loaded perpendicularly to, or in line with the securing but when axially loaded joints are involved it is more
axis. Working loads on ball joints depend upon the convenient to use the area factor throughout and Fig. 14.6
application, the working pressures appropriate to the also shows the area factor-1/D ratio relationship for
application, the materials of the contacting surfaces and axially loaded joints.
their lubrication, the area factor of the joint and its size.
The area factor, which is the projected area of the tropical
belt of width L divided by the area of the circle of diameter
D, depends upon the ratio LID. The relationship is shown 0.8 t
in the graph (Fig. 14.6).
Transverse types are seldom symmetrical and probably /
have a near equatorial gap (Fig. 14.1) but their area
factors can be arrived at from Fig. 14.6 by addition and
PROJECTED AREA
WIDTH AXIAL LOADING
-
-
PROJECTED AREA
TRANSVERSE LOADING
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
RATIO LID
Fig. 14.5. Ball joint parameters Fig. 14.6. Area factors (a) transverse and straddle
type ball joints (b) axial type ball joints
AI 4.2