Page 1092 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 1092
TTL Levels CMOS Levels
5 V V CC = 4.5-5.5V
V CC = 5V LOW VOLTAGE
LEVELS
V V = -0.1V
3.3 V OH CC
HIGH
V CC = 2.7-3.6V V = 3.85V
IH
2.5V
V OH = 2.4V V OH = 2.4V V CC = 2.3-2.7V V = 2.5V
TH
V = 2.0V V = 2.0V V OH = 2.0V
IH
IH
V = 1.7V
V = 1.5V V = 1.5V IH V = 1.35V
TH
TH
IL
V = 1.2V
TH
V = 0.8V V = 0.8V
IL
IL
IL
V OL = 0.5V V OL = 0.2V V V = 0.7V V OL = 0.1V
= 0.2V
OL
Logic Level Specifications
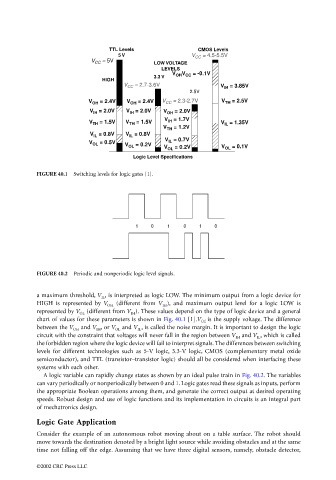
FIGURE 40.1 Switching levels for logic gates [1].
1 0 1 0 1 0
FIGURE 40.2 Periodic and nonperiodic logic level signals.
a maximum threshold, V IL , is interpreted as logic LOW. The minimum output from a logic device for
HIGH is represented by V OH (different from V IH ), and maximum output level for a logic LOW is
represented by V OL (different from V IH ). These values depend on the type of logic device and a general
chart of values for these parameters is shown in Fig. 40.1 [1].V CC is the supply voltage. The difference
between the V OH and V IH , or V OL and V IL , is called the noise margin. It is important to design the logic
circuit with the constraint that voltages will never fall in the region between V IH and V IL , which is called
the forbidden region where the logic device will fail to interpret signals. The differences between switching
levels for different technologies such as 5-V logic, 3.3-V logic, CMOS (complementary metal oxide
semiconductor), and TTL (transistor–transistor logic) should all be considered when interfacing these
systems with each other.
A logic variable can rapidly change states as shown by an ideal pulse train in Fig. 40.2. The variables
can vary periodically or nonperiodically between 0 and 1. Logic gates read these signals as inputs, perform
the appropriate Boolean operations among them, and generate the correct output at desired operating
speeds. Robust design and use of logic functions and its implementation in circuits is an integral part
of mechatronics design.
Logic Gate Application
Consider the example of an autonomous robot moving about on a table surface. The robot should
move towards the destination denoted by a bright light source while avoiding obstacles and at the same
time not falling off the edge. Assuming that we have three digital sensors, namely, obstacle detector,
©2002 CRC Press LLC