Page 1096 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 1096
R D
D
N
+
+ +
G
+ P -
+
+
D
N
-
S
+
G
S
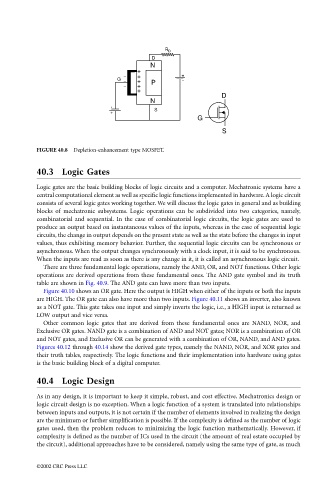
FIGURE 40.8 Depletion-enhancement type MOSFET.
40.3 Logic Gates
Logic gates are the basic building blocks of logic circuits and a computer. Mechatronic systems have a
central computational element as well as specific logic functions implemented in hardware. A logic circuit
consists of several logic gates working together. We will discuss the logic gates in general and as building
blocks of mechatronic subsystems. Logic operations can be subdivided into two categories, namely,
combinatorial and sequential. In the case of combinatorial logic circuits, the logic gates are used to
produce an output based on instantaneous values of the inputs, whereas in the case of sequential logic
circuits, the change in output depends on the present state as well as the state before the changes in input
values, thus exhibiting memory behavior. Further, the sequential logic circuits can be synchronous or
asynchronous. When the output changes synchronously with a clock input, it is said to be synchronous.
When the inputs are read as soon as there is any change in it, it is called an asynchronous logic circuit.
There are three fundamental logic operations, namely the AND, OR, and NOT functions. Other logic
operations are derived operations from these fundamental ones. The AND gate symbol and its truth
table are shown in Fig. 40.9. The AND gate can have more than two inputs.
Figure 40.10 shows an OR gate. Here the output is HIGH when either of the inputs or both the inputs
are HIGH. The OR gate can also have more than two inputs. Figure 40.11 shows an inverter, also known
as a NOT gate. This gate takes one input and simply inverts the logic, i.e., a HIGH input is returned as
LOW output and vice versa.
Other common logic gates that are derived from these fundamental ones are NAND, NOR, and
Exclusive OR gates. NAND gate is a combination of AND and NOT gates; NOR is a combination of OR
and NOT gates, and Exclusive OR can be generated with a combination of OR, NAND, and AND gates.
Figures 40.12 through 40.14 show the derived gate types, namely the NAND, NOR, and XOR gates and
their truth tables, respectively. The logic functions and their implementation into hardware using gates
is the basic building block of a digital computer.
40.4 Logic Design
As in any design, it is important to keep it simple, robust, and cost effective. Mechatronics design or
logic circuit design is no exception. When a logic function of a system is translated into relationships
between inputs and outputs, it is not certain if the number of elements involved in realizing the design
are the minimum or further simplification is possible. If the complexity is defined as the number of logic
gates used, then the problem reduces to minimizing the logic function mathematically. However, if
complexity is defined as the number of ICs used in the circuit (the amount of real estate occupied by
the circuit), additional approaches have to be considered, namely using the same type of gate, as much
©2002 CRC Press LLC