Page 1173 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 1173
those used for high-velocity turbulent flows. Still another consideration is confinement of the flow. Whereas
most fluid flow measurements are concerned with full flow through closed channels such as ducts and
pipes, some applications require measurements of partial flow through open channels such as troughs and
flumes. Only the most widely used flowmeters are considered here.
The major categories of flowmeters are:
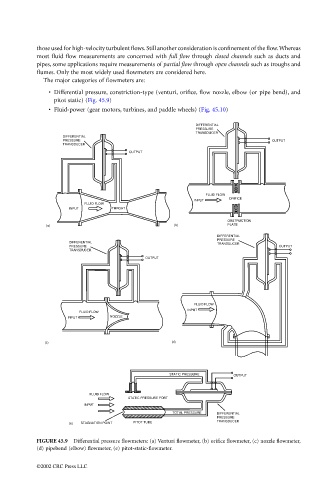
• Differential pressure, constriction-type (venturi, orifice, flow nozzle, elbow (or pipe bend), and
pitot static) (Fig. 45.9)
• Fluid-power (gear motors, turbines, and paddle wheels) (Fig. 45.10)
DIFFERENTIAL
PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
DIFFERENTIAL
PRESSURE OUTPUT
TRANSDUCER
OUTPUT
FLUID FLOW
ORIFICE
INPUT
FLUID FLOW
INPUT THROAT
OBSTRUCTION
(a) (b) PLATE
DIFFERENTIAL
PRESSURE
DIFFERENTIAL TRANSDUCER
PRESSURE OUTPUT
TRANSDUCER
OUTPUT
FLUID FLOW
INPUT
FLUID FLOW
INPUT NOZZLE
(c) (d)
STATIC PRESSURE OUTPUT
FLUID FLOW
STATIC PRESSURE PORT
INPUT
TOTAL PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL
(e) STAGNATION POINT PITOT TUBE PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
FIGURE 45.9 Differential pressure flowmeters: (a) Venturi flowmeter, (b) orifice flowmeter, (c) nozzle flowmeter,
(d) pipebend (elbow) flowmeter, (e) pitot-static-flowmeter.
©2002 CRC Press LLC