Page 1171 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 1171
ANGULAR
MOTION OUTPUT
SENSOR
PRECESSION
DISPLACEMENT
SENSOR OUTPUT INERTIAL TORQUE
REFERENCE
SPIN AXIS
ELEMENT
INPUT
F GIMBALS
F
∆θ ∆y
INPUT
SPIN
PIVOT AXIS
SPRING
PRECESSION
(a) (b) AXIS
OUTPUT
INPUT
F
(c)
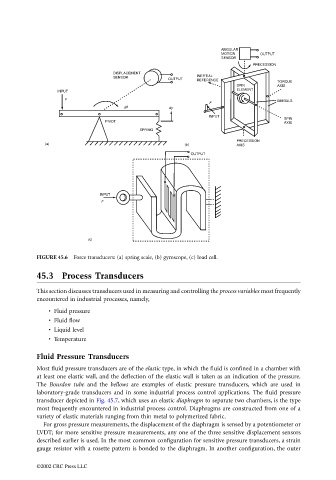
FIGURE 45.6 Force transducers: (a) spring scale, (b) gyroscope, (c) load cell.
45.3 Process Transducers
This section discusses transducers used in measuring and controlling the process variables most frequently
encountered in industrial processes, namely,
• Fluid pressure
• Fluid flow
• Liquid level
•Temperature
Fluid Pressure Transducers
Most fluid pressure transducers are of the elastic type, in which the fluid is confined in a chamber with
at least one elastic wall, and the deflection of the elastic wall is taken as an indication of the pressure.
The Bourdon tube and the bellows are examples of elastic pressure transducers, which are used in
laboratory-grade transducers and in some industrial process control applications. The fluid pressure
transducer depicted in Fig. 45.7, which uses an elastic diaphragm to separate two chambers, is the type
most frequently encountered in industrial process control. Diaphragms are constructed from one of a
variety of elastic materials ranging from thin metal to polymerized fabric.
For gross pressure measurements, the displacement of the diaphragm is sensed by a potentiometer or
LVDT; for more sensitive pressure measurements, any one of the three sensitive displacement sensors
described earlier is used. In the most common configuration for sensitive pressure transducers, a strain
gauge resistor with a rosette pattern is bonded to the diaphragm. In another configuration, the outer
©2002 CRC Press LLC