Page 587 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 587
0066_Frame_C20 Page 57 Wednesday, January 9, 2002 5:49 PM
Diaphragm
PZT Electrodes
PZT
Platform
Valves
L c
R PZT Input Output
(a) (b) (c)
Flexible Platform
PZT
PZT Channel to Dossage Nozzle
PZT reservoir chamber
(d) (e) (f)
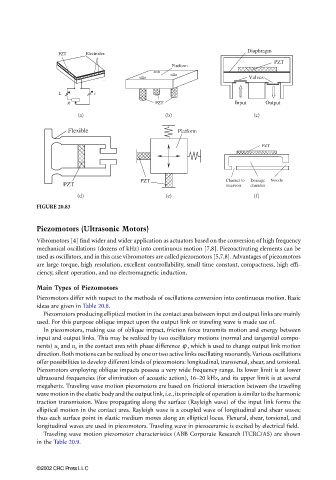
FIGURE 20.83
Piezomotors (Ultrasonic Motors)
Vibromotors [4] find wider and wider application as actuators based on the conversion of high frequency
mechanical oscillations (dozens of kHz) into continuous motion [7,8]. Piezoactivating elements can be
used as oscillators, and in this case vibromotors are called piezomotors [5,7,8]. Advantages of piezomotors
are large torque, high resolution, excellent controllability, small time constant, compactness, high effi-
ciency, silent operation, and no electromagnetic induction.
Main Types of Piezomotors
Piezomotors differ with respect to the methods of oscillations conversion into continuous motion. Basic
ideas are given in Table 20.8.
Piezomotors producing elliptical motion in the contact area between input and output links are mainly
used. For this purpose oblique impact upon the output link or traveling wave is made use of.
In piezomotors, making use of oblique impact, friction force transmits motion and energy between
input and output links. This may be realized by two oscillatory motions (normal and tangential compo-
nents) u y and u x in the contact area with phase difference , which is used to change output link motionϕ
direction. Both motions can be realized by one or two active links oscillating resonantly. Various oscillations
offer possibilities to develop different kinds of piezomotors: longitudinal, transversal, shear, and torsional.
Piezomotors employing oblique impacts possess a very wide frequency range. Its lower limit is at lower
ultrasound frequencies (for elimination of acoustic action), 16–20 kHz, and its upper limit is at several
megahertz. Traveling wave motion piezomotors are based on frictional interaction between the traveling
wave motion in the elastic body and the output link, i.e., its principle of operation is similar to the harmonic
traction transmission. Wave propagating along the surface (Rayleigh wave) of the input link forms the
elliptical motion in the contact area. Rayleigh wave is a coupled wave of longitudinal and shear waves;
thus each surface point in elastic medium moves along an elliptical locus. Flexural, shear, torsional, and
longitudinal waves are used in piezomotors. Traveling wave in piezoceramic is excited by electrical field.
Traveling wave motion piezomotor characteristics (ABB Corporate Research ITCRC/AS) are shown
in the Table 20.9.
©2002 CRC Press LLC