Page 165 - Theory and Design of Air Cushion Craft
P. 165
148 Stability
Table 4.3 The variable range of a, B
a(°) 45 45 50 50 55 55 60 60 60
B(m) 0.16 0.18 0.16 0.18 0.16 0.18 0.16 0.18 0.20
0.166 0.171 0.146 0.152 0.13 0.135 0.115 0.121 0.126
BJB e
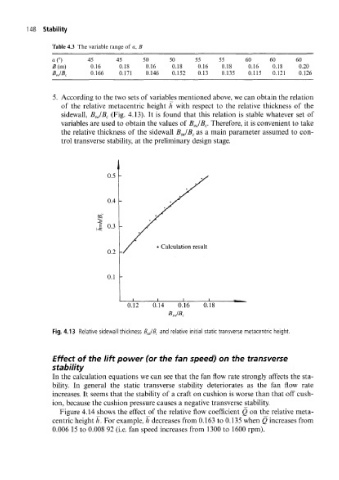
5. According to the two sets of variables mentioned above, we can obtain the relation
of the relative metacentric height h with respect to the relative thickness of the
sidewall, BJB C (Fig. 4.13). It is found that this relation is stable whatever set of
variables are used to obtain the values of BJB C. Therefore, it is convenient to take
the relative thickness of the sidewall B SW/B C as a main parameter assumed to con-
trol transverse stability, at the preliminary design stage.
0.5 -
0.4
0.3
Calculation result
0.2
0.1
0.12 0.14 0.16 0.18
BJB C
Fig. 4.13 Relative sidewall thickness BJB C and relative initial static transverse metacentric height.
Effect of the lift power (or the fan speed) on the transverse
stability
In the calculation equations we can see that the fan flow rate strongly affects the sta-
bility. In general the static transverse stability deteriorates as the fan flow rate
increases. It seems that the stability of a craft on cushion is worse than that off cush-
ion, because the cushion pressure causes a negative transverse ^ability.
Figure 4.14 ^hows the effectj)f the relative flow coefficient Q on the relative meta-
centric height h. For example, h decreases from 0.163 to 0.135 when Q increases from
0.006 15 to 0.008 92 (i.e. fan speed increases from 1300 to 1600 rpm).