Page 440 - Thomson, William Tyrrell-Theory of Vibration with Applications-Taylor _ Francis (2010)
P. 440
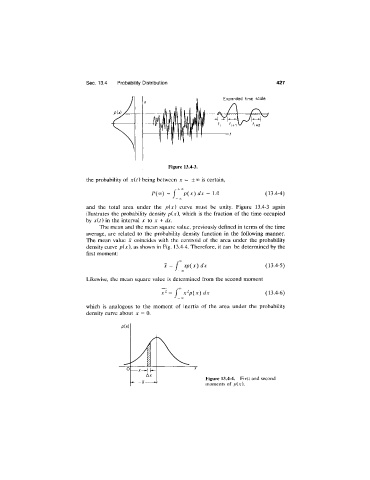
Sec. 13.4 Probability Distribution 427
the probability of x(t) being between jc = ±oc is certain,
P(oo) = i p{x) dx = 1.0 (13.4-4)
and the total area under the p{x) curve must be unity. Figure 13.4-3 again
illustrates the probability density p(x), which is the fraction of the time occupied
by jc(0 in the interval x to x dx.
The mean and the mean square value, previously defined in terms of the time
average, are related to the probability density function in the following manner.
The mean value x coincides with the centroid of the area under the probability
density curve p(x), as shown in Fig. 13.4-4. Therefore, it can be determined by the
first moment:
jc = / xp{x) dx (13.4-5)
Likewise, the mean square value is determined from the second moment
---- .00
x^ == j x^p(x) dx (13.4-6)
which is analogous to the moment of inertia of the area under the probability
density curve about jc = 0.
Figure 13.4-4. First and second
moments of p(x).