Page 71 - Thomson, William Tyrrell-Theory of Vibration with Applications-Taylor _ Francis (2010)
P. 71
58 Harmonically Excited Vibration Chap. 3
Figure 3.2-3.
When COis very much greater than the same equation becomes
X = ^ = 0.08 cm
M
By solving the two equations simultaneously, the damping factor of the system is
0.08
2 X 0.60 = 0.0666
3.3 ROTOR UNBALANCE
In Sec. 3.2 the system was idealized to a spring-mass-damper unit with a rotating
unbalance acting in a single plane, It is more likely that the unbalance in a rotating
wheel or rotor is distributed in several planes. We wish now to distinguish between
two types of rotating unbalance.
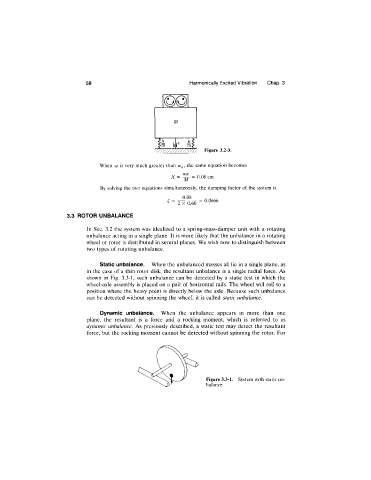
Static unbalance. When the unbalanced masses all lie in a single plane, as
in the case of a thin rotor disk, the resultant unbalance is a single radial force. As
shown in Fig. 3.3-1, such unbalance can be detected by a static test in which the
wheel-axle assembly is placed on a pair of horizontal rails. The wheel will roll to a
position where the heavy point is directly below the axle. Because such unbalance
can be detected without spinning the wheel, it is called static unbalance.
Dynamic unbalance. When the unbalance appears in more than one
plane, the resultant is a force and a rocking moment, which is referred to as
dynamic unbalance. As previously described, a static test may detect the resultant
force, but the rocking moment cannot be detected without spinning the rotor. For
Figure 3.3-1. System with static un-
balance.