Page 131 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 131
128 Chapter 7 Thermodynamics of the Binding of Ligands by Proteins
Table 7.3 Standard Transformed Gibbs Energy of Formation A,G" and Standard Further Transformed Gibbs Energies
of Formation A,G"O of Hemoglobin Dimer at 21.5'C, 1 bar, pH 7.4, [Cl-] = 0.2M, and 0.2M Ionic Strength
A,G"'(TotD),'kJ mol
A,G"(TotD)/kJ mol- [O,] = 5 x lo-' M [0,]=10-' M [02]=2x 10PM
D 30.083 25 30.083 25 30.083 25 30.083 25
D(O2) 9.447 23 23.250 50 21.552 40 19.854 30
D(O,), -7.799 32 19.807 30 16.411 00 13.014 80
A,G""(TotD)/kJ mol- 19.240 4 16.119 4 12.866 8
ArG"O(eq 7.3-4)/kJ mol - 33.772 6% -39.217 3 -35.053 7 -33.802 7
K"(eq. 7.3-7) 9.508 x lo'* 8.956 x lo6 1.637 x lo6 0.982 x 10'
Source: Reprinted from R. A. Alberty, Biophys. Cliern. 62, 141-159 (1996), with permission from Elsevier Science.
Note: See Problem 7.2.
The corresponding binding polynomial for dimer is given by
P, = 1 + K;,[O,] + K;,[O,]' (7.3-5)
Thermodynamic properties of dimmers are summarized in Table 7.3.
The fractional saturation of dimer Y, is given by the Adair equation (see
equation 7.1-18)
(7.3-6)
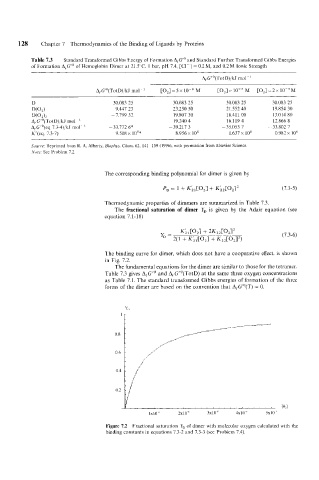
The binding curve for dimer, which does not have a cooperative effect. is shown
in Fig. 7.2.
The fundamental equations for the dimer are similar to those for the tetramer.
Table 7.3 gives AfG"' and A,G"'(TotD) at the same three oxygen concentrations
as Table 7.1. The standard transformed Gibbs energies of formation of the three
forms of the dimer are based on the convention that AfG"(T) = 0.
1x10" 2x10" 3x10" 4x 10 -I3 5x10"
Figure 7.2 Fractional saturation Y, of dimer with molecular oxygen calculated with the
binding constants in equations 7.3-2 and 7.3-3 (see Problem 7.4).