Page 221 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 221
BasicBiochemData2 221
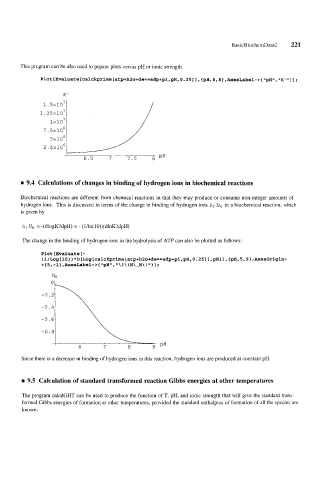
This program can be also used to pepare plots versus pH or ionic strength.
Plot [Evaluate[calckprime~atp+h2o+de==adp+p~,pH,O.2511, CpH, 6,8},AxesLabel->{"pH", "K"'l1 i
K'
I
6.5 7 7.5 8 PH
rn 9.4 Calculations of changes in binding of hydrogen ions in biochemical reactions
Biochemical reactions are different from chemical reactions in that they may produce or consume non-integer amounts of
hydrogen ions. This is discussed in terms of the change in binding of hydrogen ions af NH in a biochemical reaction, which
is given by
A, NH = -(dlogK/dpH) = - (l/ln(lO))(dlnK'/dpH)
The change in the binding of hydrogen ions in the hydrolysis of ATP can also be plotted as follows:
Plot [Evaluate [ -
~1/Log[lO])*D[Log[caIckgrime[atg+h20+de==adp+~~,pH,O.25]],pH]l,~~H,~,9~,~esOrigin-
C
> C 5, -1 1, AxesLabel-> "pH", I \ (N\-H\ ) 1 1 ;
-0.
-0.
-0.
-0.
Since there is a decrease in binding of hydrogen ions in this reaction, hydrogen ions are produced at constant pH.
9.5 Calculation of standard transformed reaction Gibbs energies at other temperatures
The program calcdGHT can be used to produce the function of T, pH, and ionic strength that will give the standard trans-
formed Gibbs energies of formation at other temperatures, provided the standard enthalpies of formation of all the species are
known.