Page 211 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 211
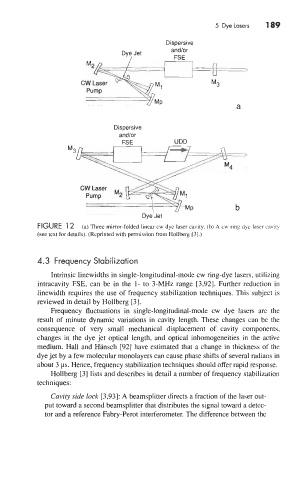
5 Dye Lasers 189
Dispersive
and/or
Dye Jet
FSE
C
a
Dispersive
and/or
FSE UDD
Dye Jet
FIGURE 1 2 (a) Three mirror-folded linear cw dye laser cavity. (b) A cw ring dye laser cavity
(see text for details). (Reprinted with permission from Hollberg [3].)
4.3 Frequency Stabilization
Intrinsic linewidths in single-longitudinal-mode cw ring-dye lasers, utilizing
intracavity FSE, can be in the 1- to 3-MHz range [3,92]. Further reduction in
linewidth requires the use of frequency stabilization techniques. This subject is
reviewed in detail by Hollberg [3].
Frequency fluctuations in single-longitudinal-mode cw dye lasers are the
result of minute dynamic variations in cavity length. These changes can be the
consequence of very small mechanical displacement of cavity components,
changes in the dye jet optical length, and optical inhomogeneities in the active
medium. Hall and Hksch [92] have estimated that a change in thickness of the
dye jet by a few molecular monolayers can cause phase shifts of several radians in
about 3 ps. Hence, frequency stabilization techniques should offer rapid response.
Hollberg [3] lists and describes in detail a number of frequency stabilization
techniques:
Cavity side lock 13,931: A beamsplitter directs a fraction of the laser out-
put toward a second beamsplitter that distributes the signal toward a detec-
tor and a reference Fabry-Perot interferometer. The difference between the