Page 215 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 215
5 Dye Lasers 193
R=5cm
lntracavity Quartz Prisms
Translation Stage
a
b
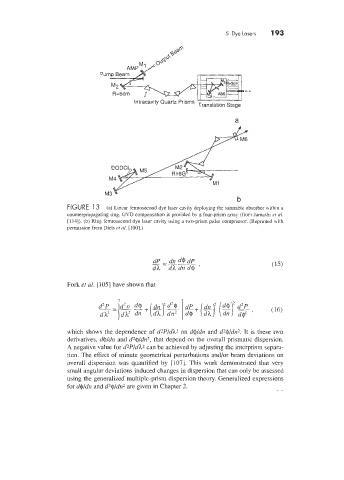
FIGURE 1 3 (a) Linear femtosecond dye laser cavity deploying the saturable absorber \+ithin a
counterpropagating ring. GVD compensation is provided by a four-prism array (from Jamasbi cr al.
[114]). (b) Ring femtosecond dye laser cavity using a two-prism pulse compressor. (Reprinted with
permission from Diels er al. [loo].)
Fork et al. [ 1051 have shown that
which shows the dependence of d’P/dhl on d@/dn and d2@/dii2. It is these two
derivatives, d@ldn and d~@/dn~, depend on the overall prismatic dispersion.
that
A negative value for dT/dhz can be achieved by adjusting the interprism separa-
lion. The effect of minute geometrical perturbations and/or beam deviations on
overall dispersion was quantified by [107]. This work demonstrated that very
small angular deviations induced changes in dispersion that can only be assessed
using the generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory. Generalized expressions
for d@/dn and &@/dnL xe given in Chapter 2.