Page 216 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 216
194 F. J. Duarte
Kafka and Baer [lo81 and Duarte [lo71 have discussed the effect of varia-
tions of beam angle of exit and incidence on overall dispersion. Bor [I091 has
considered the distortion of femtosecond pulses following transmission in lens
sys tems.
The first Qse of intracavity prismatic dispersion to achieve pulse compres-
sion was reported by Dietel et al. [ 1151. These authors reported pulse lengths of
less than 60 fs. A collinear four-prism sequence was introduced by Fork et al.
[lOS] and a single prism pair was used by Diels et al. [ 1001. The dispersion the-
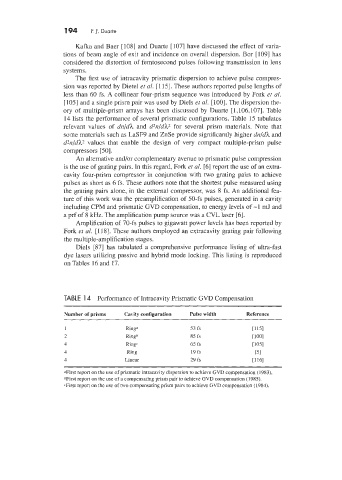
ory of multiple-prism arrays has been discussed by Duarte [1,106.107]. Table
14 lists the performance of several prismatic configurations. Table 15 tabulates
relevant values of dn/dh and d*n/dhz for several prism materials. Note that
some materials such as LaSF9 and ZnSe provide significantly higher drildh and
8n/dh? values that enable the design of very compact multiple-prism pulse
compressors [SO].
An alternative and/or complementary avenue to prismatic pulse compression
is the use of grating pairs. In this regard, Fork et al. [6] report the use of an extra-
cavity four-prism compressor in conjunction with two grating pairs to achieve
pulses as short as 6 fs. These authors note that the shortest pulse measured using
the grating pairs alone, in the external compressor, was 8 fs. An additional fea-
ture of this work was the preamplification of 50-fs pulses, generated in a cavity
including CPM and prismatic GVD compensation, to energy levels of - 1 mJ and
a prf of 8 kHz. The amplification pump source was a CVL laser [6].
Amplification of 70-fs pulses to gigawatt power levels has been reported by
Fork et al. [118]. These authors employed an extracavity grating pair following
the multiple-amplification stages.
Diels [87] has tabulated a comprehensive performance listing of ultra-fast
dye lasers utilizing passive and hybrid mode locking. This listing is reproduced
on Tables 16 and 17.
TABLE 14 Performance of Intracavity Prismatic GVD Compensation
~~
Number of prisms Cavity configuration Pulse width Reference
Ring0 53 fs
Ringh 85 fs
Ringc 65 fs
Ring 19 fs
Linear 29 fs
aFirst report on the use of prismatic inuacavity dispersion to achieve GVD compensation (1983).
bFirst report on the use of a compensating prism pair to achieve GVD compensation (1985).
<First report on the use of two compensating prism pairs to achieve GVD compensation (1984).