Page 206 - Understanding Automotive Electronics
P. 206
2735 | CH 6 Page 193 Tuesday, March 10, 1998 1:10 PM
SENSORS AND ACTUATORS 6
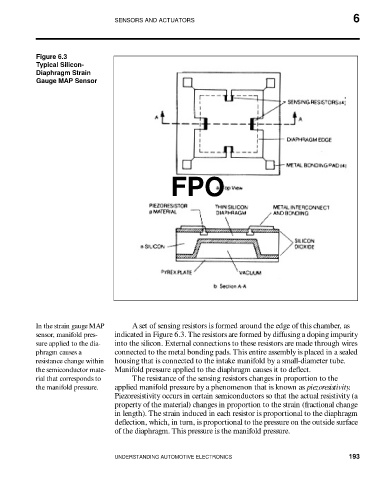
Figure 6.3
Typical Silicon-
Diaphragm Strain
Gauge MAP Sensor
FPO
In the strain gauge MAP A set of sensing resistors is formed around the edge of this chamber, as
sensor, manifold pres- indicated in Figure 6.3. The resistors are formed by diffusing a doping impurity
sure applied to the dia- into the silicon. External connections to these resistors are made through wires
phragm causes a connected to the metal bonding pads. This entire assembly is placed in a sealed
resistance change within housing that is connected to the intake manifold by a small-diameter tube.
the semiconductor mate- Manifold pressure applied to the diaphragm causes it to deflect.
rial that corresponds to The resistance of the sensing resistors changes in proportion to the
the manifold pressure. applied manifold pressure by a phenomenon that is known as piezoresistivity.
Piezoresistivity occurs in certain semiconductors so that the actual resistivity (a
property of the material) changes in proportion to the strain (fractional change
in length). The strain induced in each resistor is proportional to the diaphragm
deflection, which, in turn, is proportional to the pressure on the outside surface
of the diaphragm. This pressure is the manifold pressure.
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS 193