Page 312 - Understanding Automotive Electronics
P. 312
2735 | CH 9 Page 299 Tuesday, March 10, 1998 1:24 PM
AUTOMOTIVE INSTRUMENTATION 9
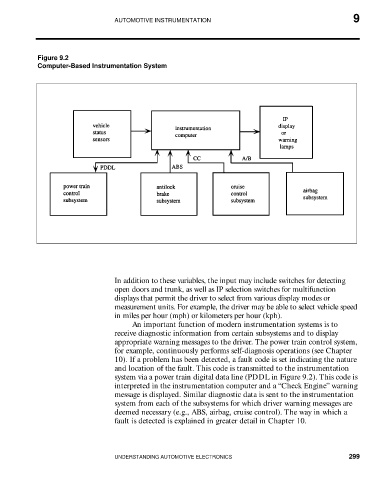
Figure 9.2
Computer-Based Instrumentation System
In addition to these variables, the input may include switches for detecting
open doors and trunk, as well as IP selection switches for multifunction
displays that permit the driver to select from various display modes or
measurement units. For example, the driver may be able to select vehicle speed
in miles per hour (mph) or kilometers per hour (kph).
An important function of modern instrumentation systems is to
receive diagnostic information from certain subsystems and to display
appropriate warning messages to the driver. The power train control system,
for example, continuously performs self-diagnosis operations (see Chapter
10). If a problem has been detected, a fault code is set indicating the nature
and location of the fault. This code is transmitted to the instrumentation
system via a power train digital data line (PDDL in Figure 9.2). This code is
interpreted in the instrumentation computer and a “Check Engine” warning
message is displayed. Similar diagnostic data is sent to the instrumentation
system from each of the subsystems for which driver warning messages are
deemed necessary (e.g., ABS, airbag, cruise control). The way in which a
fault is detected is explained in greater detail in Chapter 10.
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS 299