Page 210 - Uninterruptible Power Supplies
P. 210
Batteries
208 Chapter Seven
Readings List
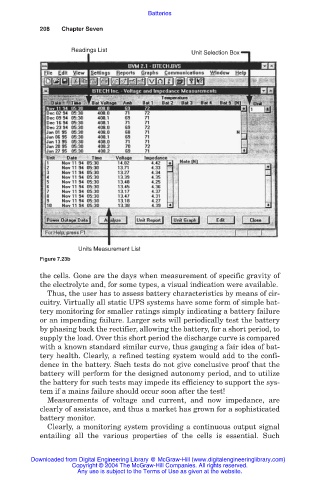
Unit Selection Box
Units Measurement List
Figure 7.23b
the cells. Gone are the days when measurement of specific gravity of
the electrolyte and, for some types, a visual indication were available.
Thus, the user has to assess battery characteristics by means of cir-
cuitry. Virtually all static UPS systems have some form of simple bat-
tery monitoring for smaller ratings simply indicating a battery failure
or an impending failure. Larger sets will periodically test the battery
by phasing back the rectifier, allowing the battery, for a short period, to
supply the load. Over this short period the discharge curve is compared
with a known standard similar curve, thus gauging a fair idea of bat-
tery health. Clearly, a refined testing system would add to the confi-
dence in the battery. Such tests do not give conclusive proof that the
battery will perform for the designed autonomy period, and to utilize
the battery for such tests may impede its efficiency to support the sys-
tem if a mains failure should occur soon after the test!
Measurements of voltage and current, and now impedance, are
clearly of assistance, and thus a market has grown for a sophisticated
battery monitor.
Clearly, a monitoring system providing a continuous output signal
entailing all the various properties of the cells is essential. Such
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.