Page 115 - Using ANSYS for Finite Element Analysis Dynamic, Probabilistic, Design and Heat Transfer Analysis
P. 115
102 • using ansys for finite eLement anaLysis
would be considered very sensitive with respect to a certain input parame-
ter if you observe a large change of the output parameter value.
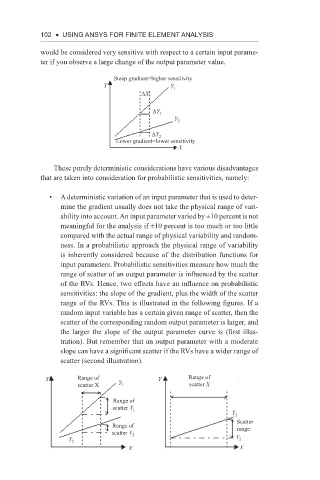
Steep gradient=higher sensitivity
Y Y 1
ΔX
ΔY 1
Y 2
ΔY 2
Lower gradient=lower sensitivity
X
These purely deterministic considerations have various disadvantages
that are taken into consideration for probabilistic sensitivities, namely:
• A deterministic variation of an input parameter that is used to deter-
mine the gradient usually does not take the physical range of vari-
ability into account. An input parameter varied by ±10 percent is not
meaningful for the analysis if ±10 percent is too much or too little
compared with the actual range of physical variability and random-
ness. In a probabilistic approach the physical range of variability
is inherently considered because of the distribution functions for
input parameters. Probabilistic sensitivities measure how much the
range of scatter of an output parameter is influenced by the scatter
of the RVs. Hence, two effects have an influence on probabilistic
sensitivities: the slope of the gradient, plus the width of the scatter
range of the RVs. This is illustrated in the following figures. If a
random input variable has a certain given range of scatter, then the
scatter of the corresponding random output parameter is larger, and
the larger the slope of the output parameter curve is (first illus-
tration). But remember that an output parameter with a moderate
slope can have a significant scatter if the RVs have a wider range of
scatter (second illustration).
Y Range of Y Range of
scatter X Y 1 scatter X
Range of
scatter Y 1
Y 2
Scatter
Range of range
scatter Y 2
Y 2 Y 2
X X