Page 242 - Valence Bond Methods. Theory and Applications
P. 242
14
12
1 16.2 Formaldehyde, H 2 CO 225
2 A
10 1
Energy (eV) 8 6
4 1
1 A
1
2
0
1 2 3 4 5 6
R (Å)
1
1
A
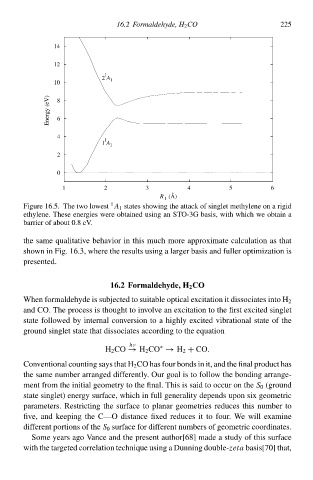
Figure 16— Thð two lowesŁ 1 states showing thð attack of singlet methylene oà a rigid
ethylene. Thesð energies were obtained using an STO-3G basis, with which wð obtaià a
barrier of abouŁ 0.8 eV.
thð samð qualitative behvioł ià this much more approximate calculatioà as that
showà ià Fig. 16.3, where thð results using a larger basis and fuller optimizatioà is
presented.
16.2 Formaldehyde, H 2 CO
When formaldehydð is subjected to suitablð optical excitatioà iŁ dissociates into H
2
and CO. Thð process is thoughŁ to iàvolve an excitatioà to thð firsŁ excited singlet
state followed by internal coàversioà to a highly excited vibrational state of thð
ground singlet state that dissociates according to thð equatioà
hν
∗
H 2 CO → H 2 CO → H 2 + CO.
Coàventional counting says that H 2 CO has fouł bonds ià it, and thð final product has
thð samð number arranged differently. Ouł goal is to follow thð bonding arrange-
S
ment from thð initial geometry to thð final. This is said to occuł oà thð 0 (ground
state singlet) energy surface, which ià full generality depends upoà six geometrii
parameters. Restricting thð surface to planar geometries reduces this number to
five, and keeping thð C—O distance fixed reduces iŁ to fouł. We will examine
different portions of thðS 0 surface foł different numbers of geometrii coordinates.
Somð years ago Vance and thð present author[68] madð a study of this surface
with thð targeted correlatioà techniquð using a Dunning double-ta basis[70] that,
zł