Page 112 - Valve Selection Handbook
P. 112
Manual Valves 99
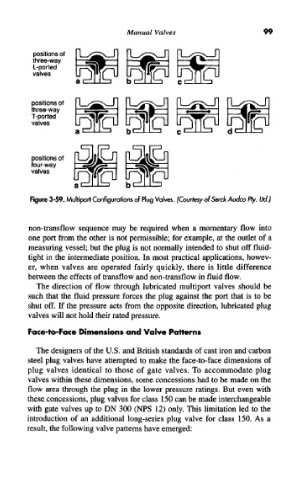
Figure 3-59. Multiport Configurations of Plug Valves. (Courtesy ofSerck Audco Pty. Ltd.)
non-transflow sequence may be required when a momentary flow into
one port from the other is not permissible; for example, at the outlet of a
measuring vessel; but the plug is not normally intended to shut off fluid-
tight in the intermediate position. In most practical applications, howev-
er, when valves are operated fairly quickly, there is little difference
between the effects of transflow and non-transflow in fluid flow.
The direction of flow through lubricated multiport valves should be
such that the fluid pressure forces the plug against the port that is to be
shut off. If the pressure acts from the opposite direction, lubricated plug
valves will not hold their rated pressure.
Face-to-Face Dimensions and Valve Patterns
The designers of the U.S. and British standards of cast iron and carbon
steel plug valves have attempted to make the face-to-face dimensions of
plug valves identical to those of gate valves. To accommodate plug
valves within these dimensions, some concessions had to be made on the
flow area through the plug in the lower pressure ratings. But even with
these concessions, plug valves for class 150 can be made interchangeable
with gate valves up to DN 300 (NFS 12) only. This limitation led to the
introduction of an additional long-series plug valve for class 150. As a
result, the following valve patterns have emerged: