Page 161 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 161
CAT3525_C06.qxd 1/29/2005 9:56 AM Page 132
132 Waste Management Practices: Municipal, Hazardous, and Industrial
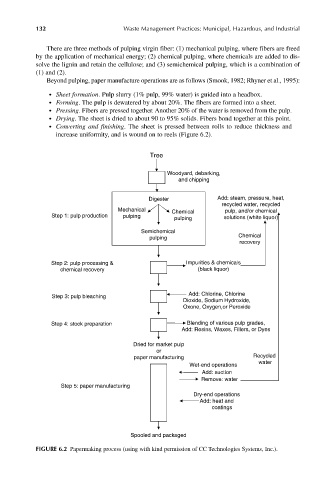
There are three methods of pulping virgin fiber: (1) mechanical pulping, where fibers are freed
by the application of mechanical energy; (2) chemical pulping, where chemicals are added to dis-
solve the lignin and retain the cellulose; and (3) semichemical pulping, which is a combination of
(1) and (2).
Beyond pulping, paper manufacture operations are as follows (Smook, 1982; Rhyner et al., 1995):
● Sheet formation. Pulp slurry (1% pulp, 99% water) is guided into a headbox.
● Forming. The pulp is dewatered by about 20%. The fibers are formed into a sheet.
● Pressing. Fibers are pressed together. Another 20% of the water is removed from the pulp.
● Drying. The sheet is dried to about 90 to 95% solids. Fibers bond together at this point.
● Converting and finishing. The sheet is pressed between rolls to reduce thickness and
increase uniformity, and is wound on to reels (Figure 6.2).
Tree
Woodyard, debarking,
and chipping
Digester Add: steam, pressure, heat,
recycled water, recycled
Mechanical Chemical pulp, and/or chemical
Step 1: pulp production pulping pulping solutions (white liquor)
Semichemical
pulping Chemical
recovery
Step 2: pulp processing & Impurities & chemicals
chemical recovery (black liquor)
Add: Chlorine, Chlorine
Step 3: pulp bleaching
Dioxide, Sodium Hydroxide,
Oxone, Oxygen,or Peroxide
Step 4: stock preparation Blending of various pulp grades,
Add: Resins, Waxes, Fillers, or Dyes
Dried for market pulp
or
paper manufacturing Recycled
water
Wet-end operations
Add: suction
Remove: water
Step 5: paper manufacturing
Dry-end operations
Add: heat and
coatings
Spooled and packaged
FIGURE 6.2 Papermaking process (using with kind permission of CC Technologies Systems, Inc.).