Page 293 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 293
CAT3525_C09.qxd 2/8/2005 10:11 AM Page 264
264 Waste Management Practices: Municipal, Hazardous, and Industrial
Raw gas
inlet
descharge
Collecting electrodes
electrode plates
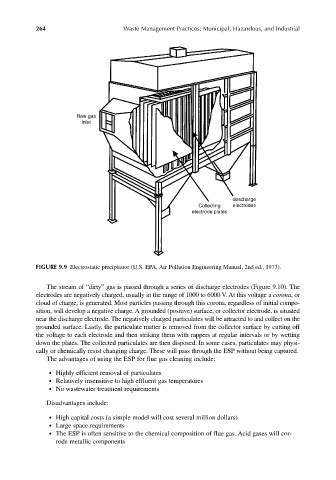
FIGURE 9.9 Electrostatic precipitator (U.S. EPA, Air Pollution Engineering Manual, 2nd ed., 1973).
The stream of “dirty” gas is passed through a series of discharge electrodes (Figure 9.10). The
electrodes are negatively charged, usually in the range of 1000 to 6000 V. At this voltage a corona,or
cloud of charge, is generated. Most particles passing through this corona, regardless of initial compo-
sition, will develop a negative charge. A grounded (positive) surface, or collector electrode, is situated
near the discharge electrode. The negatively charged particulates will be attracted to and collect on the
grounded surface. Lastly, the particulate matter is removed from the collector surface by cutting off
the voltage to each electrode and then striking them with rappers at regular intervals or by wetting
down the plates. The collected particulates are then disposed. In some cases, particulates may physi-
cally or chemically resist changing charge. These will pass through the ESP without being captured.
The advantages of using the ESP for flue gas cleaning include:
● Highly efficient removal of particulates
● Relatively insensitive to high effluent gas temperatures
● No wastewater treatment requirements
Disadvantages include:
● High capital costs (a simple model will cost several million dollars)
● Large space requirements
● The ESP is often sensitive to the chemical composition of flue gas. Acid gases will cor-
rode metallic components